Democratic Republic of the Congo Map: Political, Physical, Regions, and Cities Maps
The Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) is a vast country in the heart of Central Africa. Bordered by nine nations, it meets Angola to the southwest, Zambia to the southeast, Tanzania, Burundi and Rwanda to the east, Uganda and South Sudan to the northeast, the Republic of the Congo to the west and the Central African Republic to the northwest. The DRC also touches the Atlantic Ocean along a short western coastline, making it a strategic crossroads for regional trade and transport.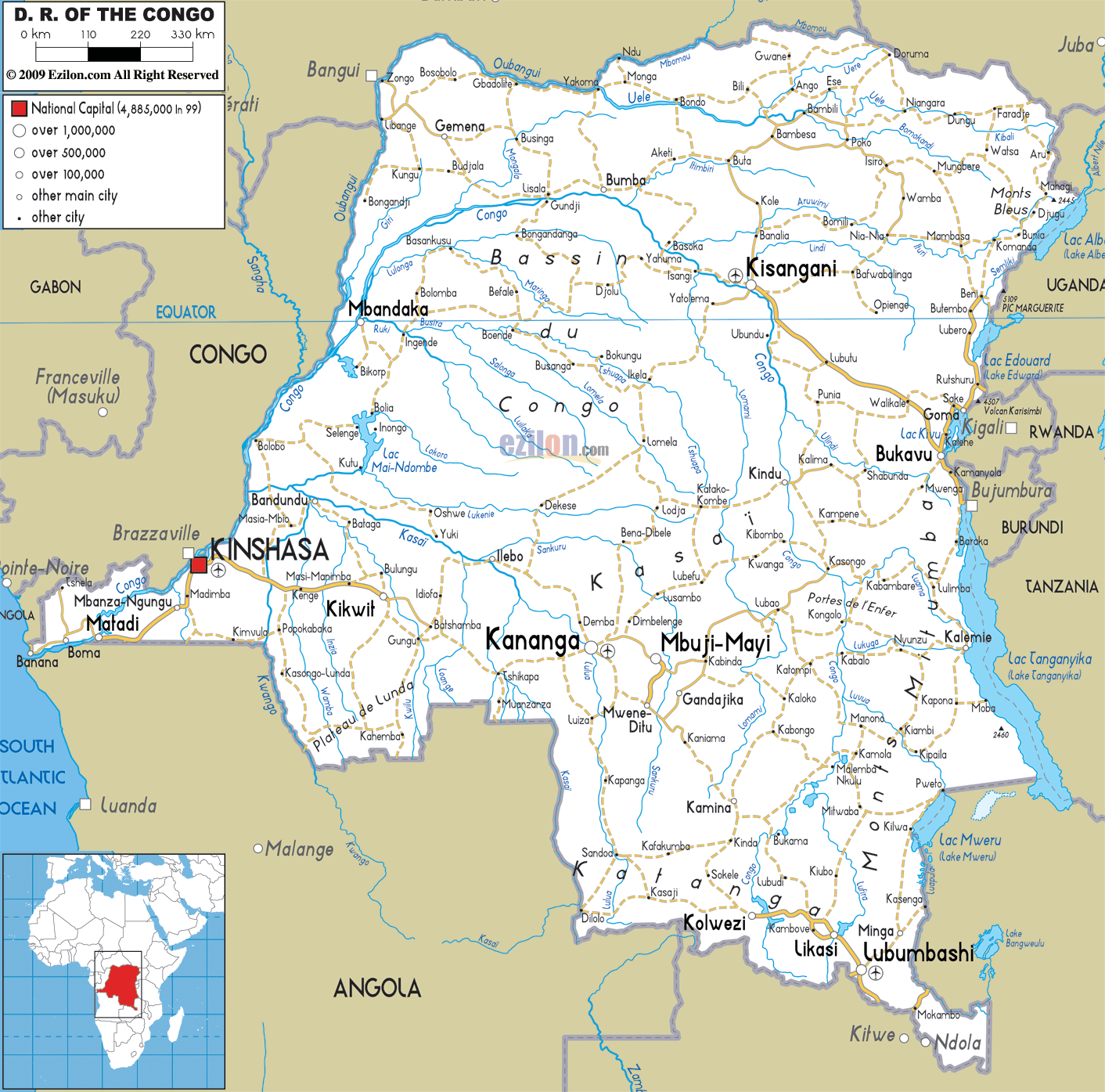
Congo physical map
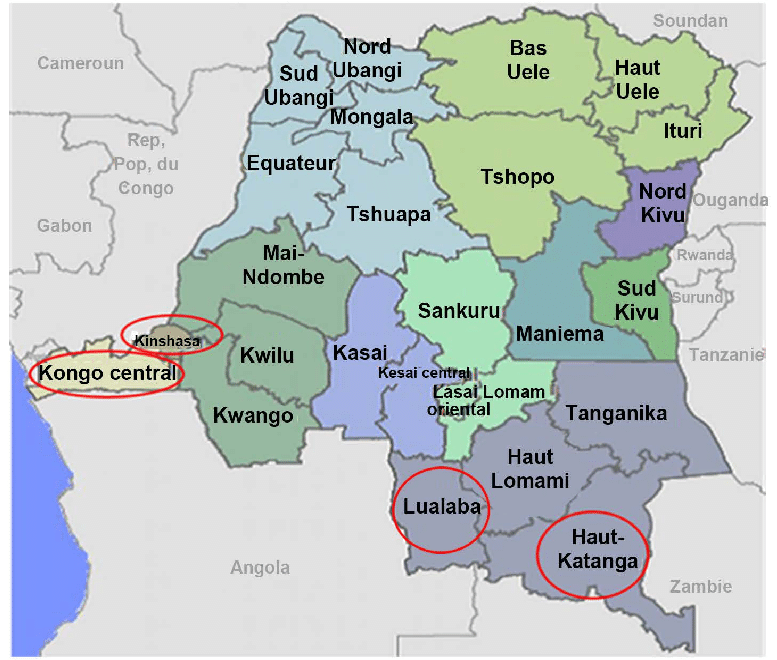
Political Congo Map
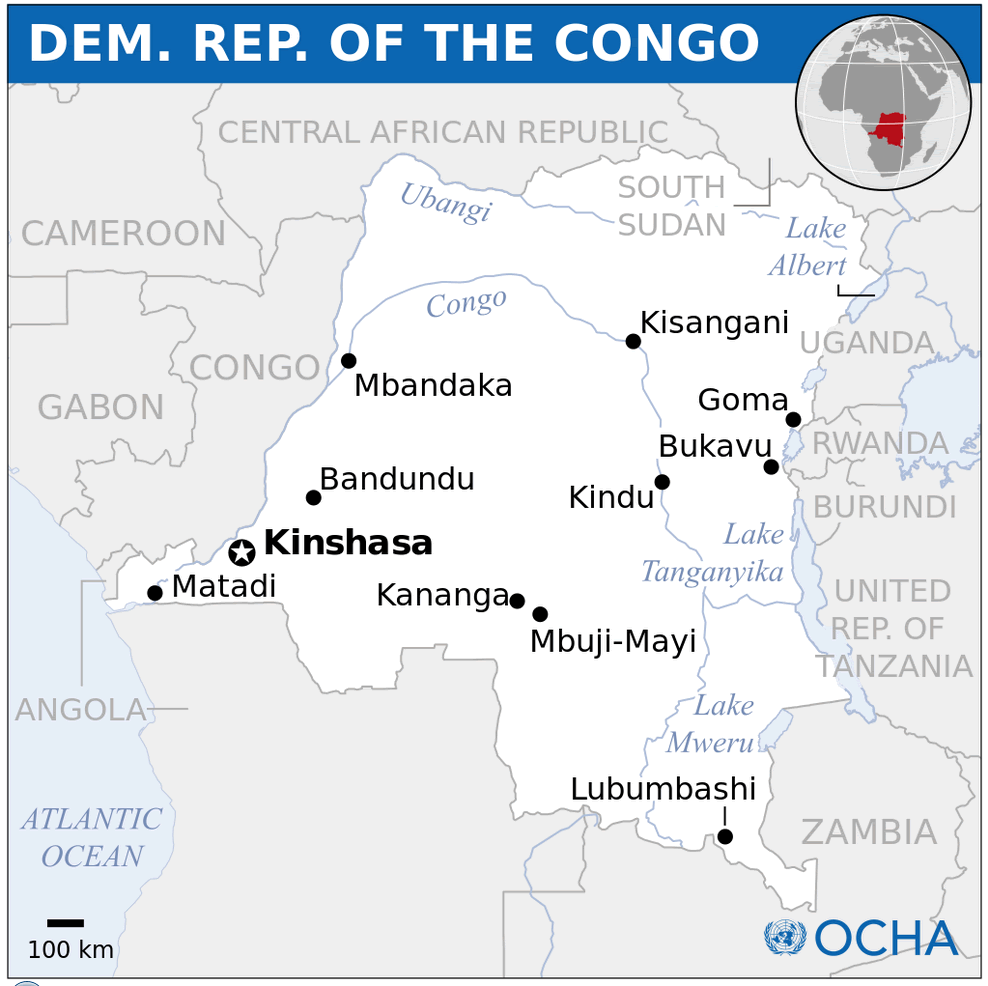
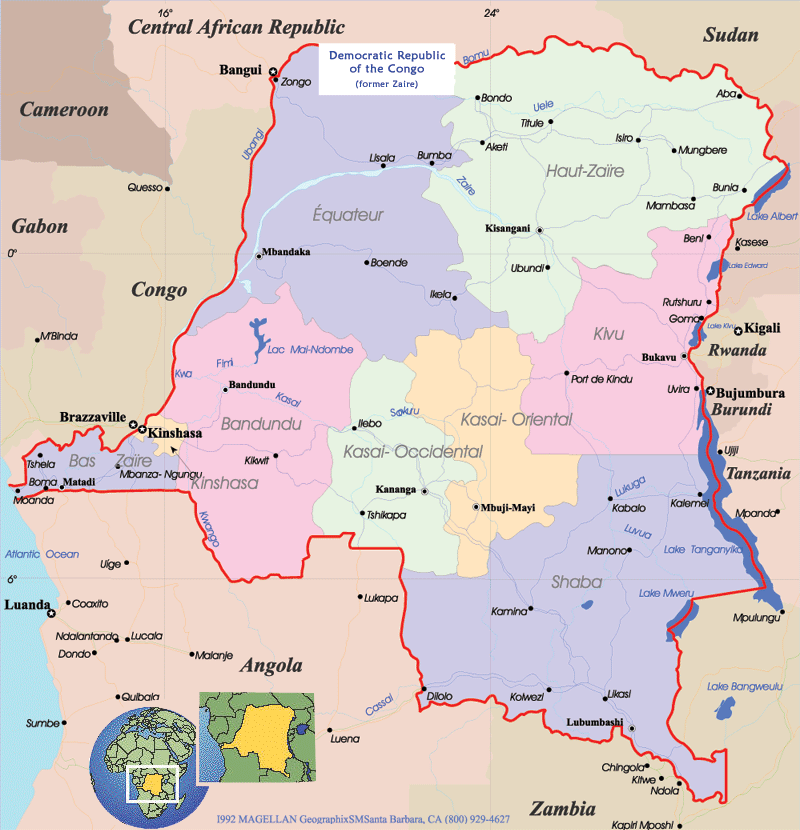 Political map of the Democratic Republic of the Congo showing provinces and neighboring countries.
Political map of the Democratic Republic of the Congo showing provinces and neighboring countries.This map provides a political overview of the DRC, highlighting its provinces, major cities, and international borders with neighboring countries, including Rwanda, Uganda, Angola, and Sudan. Key water bodies such as Lake Tanganyika and the Congo River are also displayed, emphasizing the geographic and political complexity of this vast nation.
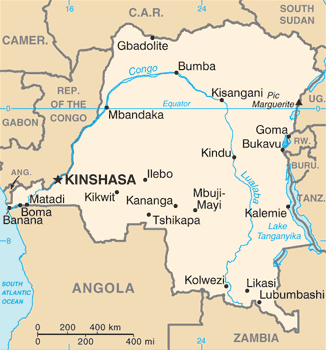
Congo Road Map — Major Routes, Cities and River Crossings
 Congo (DRC) road map showing major cities, highways and Congo River routes.
Congo (DRC) road map showing major cities, highways and Congo River routes.This road map of the Democratic Republic of the Congo displays primary and secondary highways, major urban centers (Kinshasa, Lubumbashi, Kisangani, Mbuji-Mayi), river routes along the Congo River, and key border crossings. Useful for planning travel, logistics and understanding national transport corridors.
Brief information about Democratic Republic of the Congo
The Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) is the second largest country in Africa, located in central Africa. It borders nine countries, including Angola, Zambia, Tanzania, Uganda, Rwanda and the Republic of Congo, with the Congo River running through its centre. The capital, Kinshasa, is one of the largest cities in Africa and serves as the political, cultural and economic centre of the country.
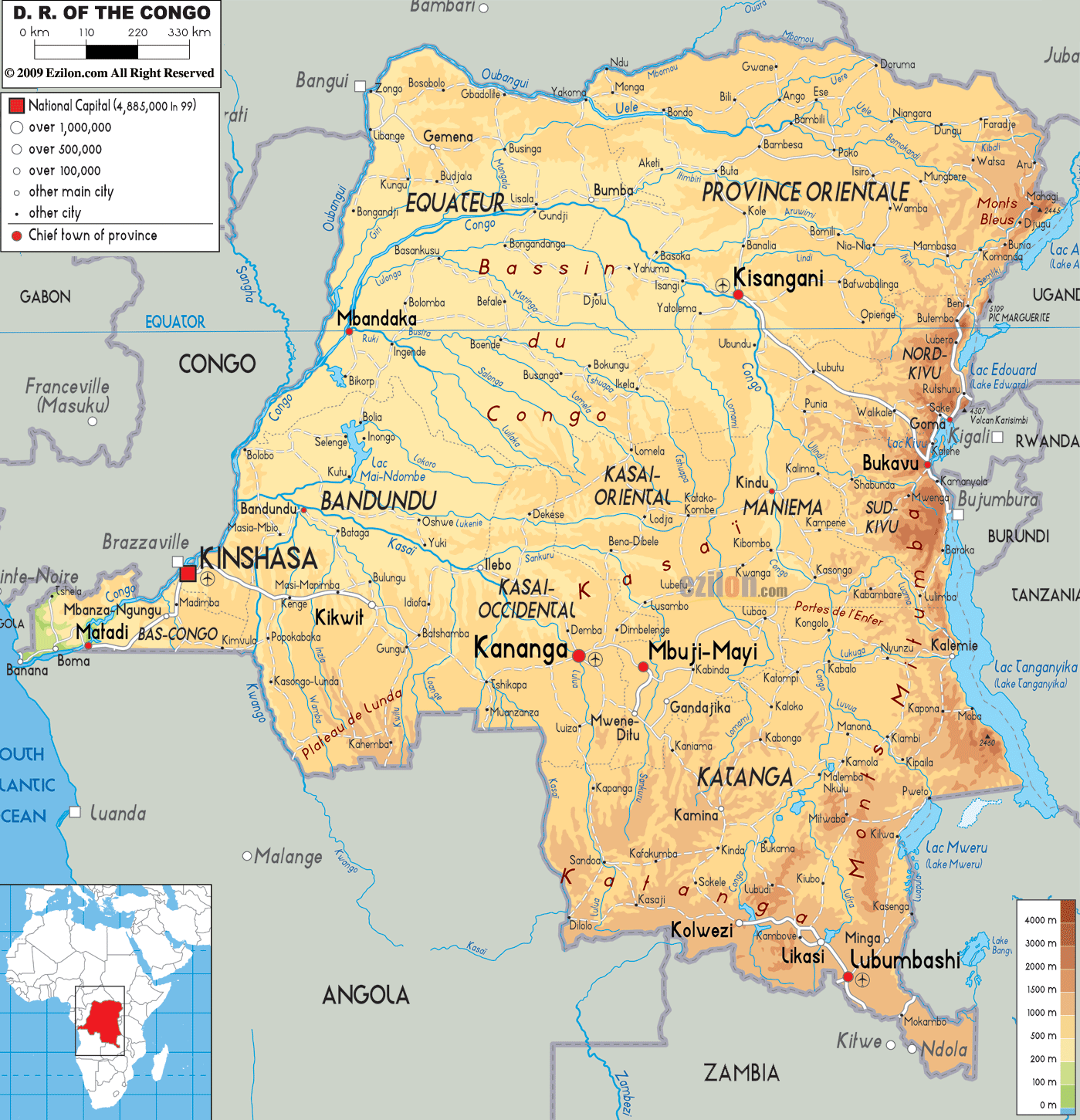
Congo political map
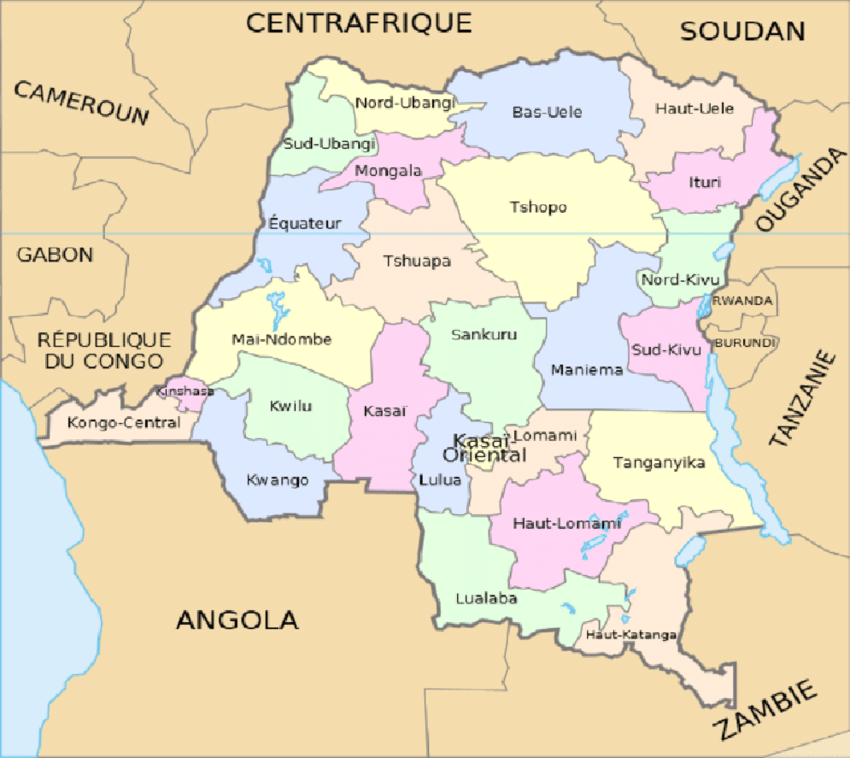
Map dr congo major
Rich in natural resources, the DRC is home to vast mineral wealth, including cobalt, copper and diamonds, making it a key player in global supply chains. The country also boasts diverse ecosystems, from dense rainforests in the Congo Basin to savannahs and volcanic mountains in the east. Despite its natural wealth, the DRC faces challenges such as political instability and economic inequality, but it remains a country of immense cultural and environmental significance.
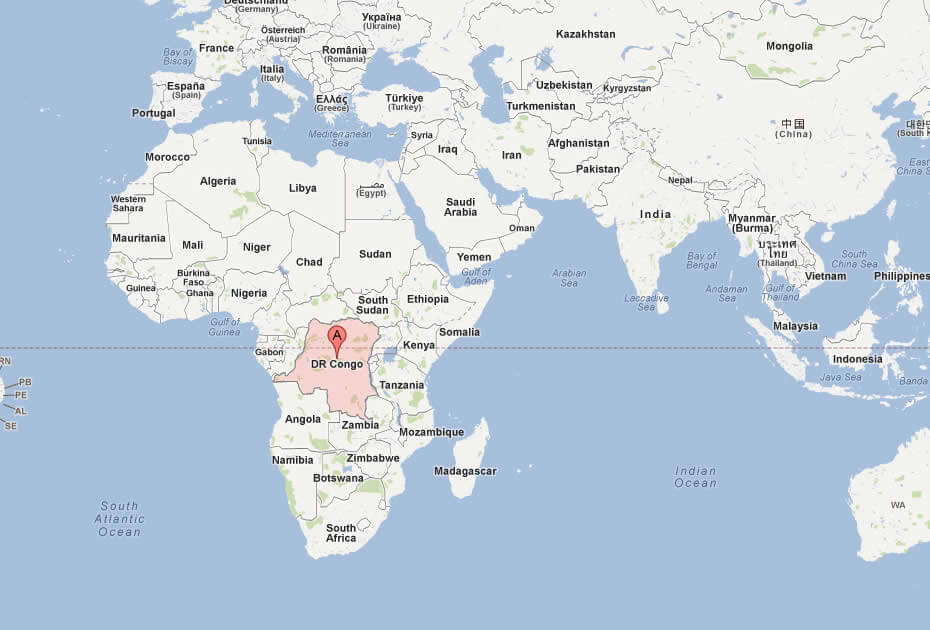
Where is located Democratic Republic of the Congo on the World and Africa Map?
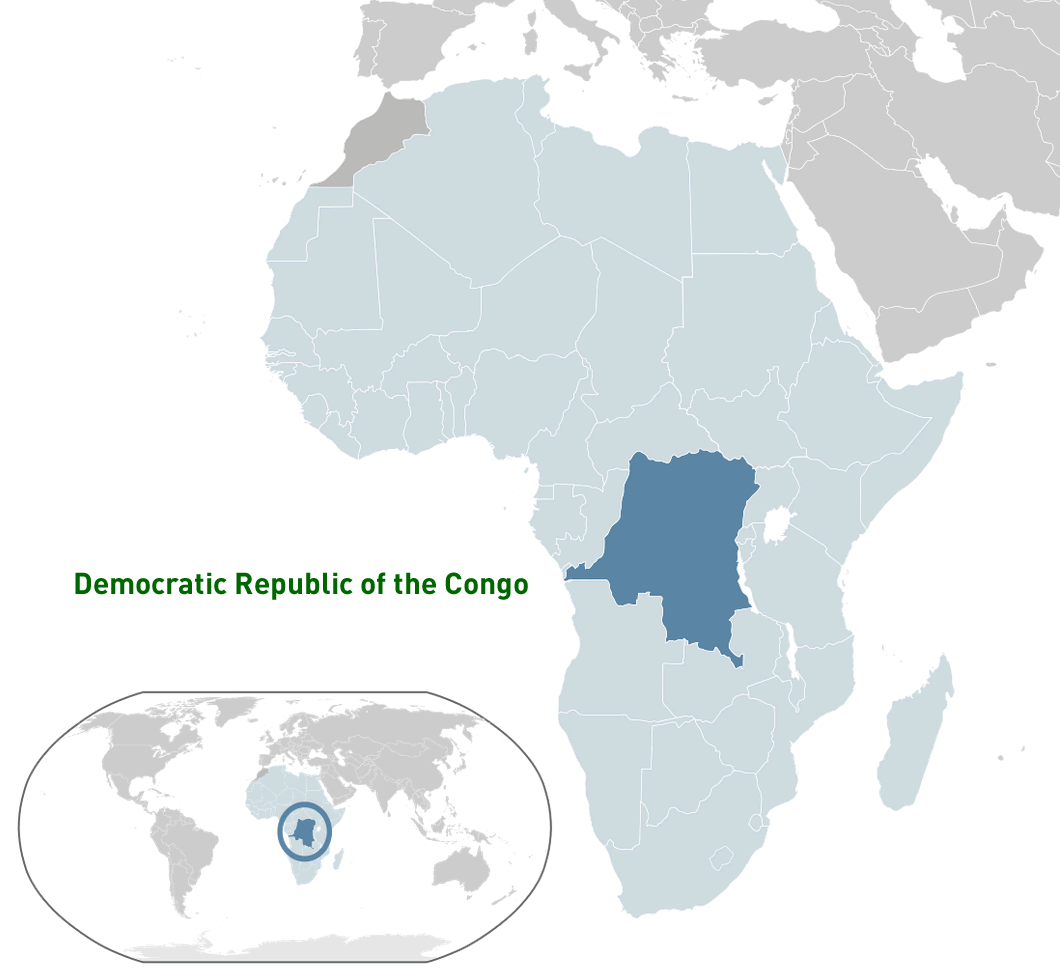 Where is located Democratic Republic of the Congo on the World Map
Where is located Democratic Republic of the Congo on the World MapThe Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) is located in the heart of Central Africa. It borders nine countries: Angola to the southwest, Zambia to the southeast, Tanzania, Burundi and Rwanda to the east, Uganda and South Sudan to the northeast, the Republic of Congo to the west and the Central African Republic to the northwest. It also has a small coastline along the Atlantic Ocean on its western border.
The country's location on the equator gives it a tropical climate and lush rainforests, particularly in the Congo Basin, which is the second largest rainforest in the world after the Amazon. The Congo River, one of the world's longest and most powerful rivers, flows through the country, playing a crucial role in transportation and supporting diverse ecosystems.
On a world map, the DRC is located in the central part of Africa, making it a geographical and ecological hub. Its vast size and natural resources, including minerals and biodiversity, underline its importance not only within Africa but also on a global scale.
Here are some statistical information about Democratic Republic of the Congo:
 Area: 2,345,409 km2 (905,567 sq mi)
Area: 2,345,409 km2 (905,567 sq mi) Koppen geiger map cod present
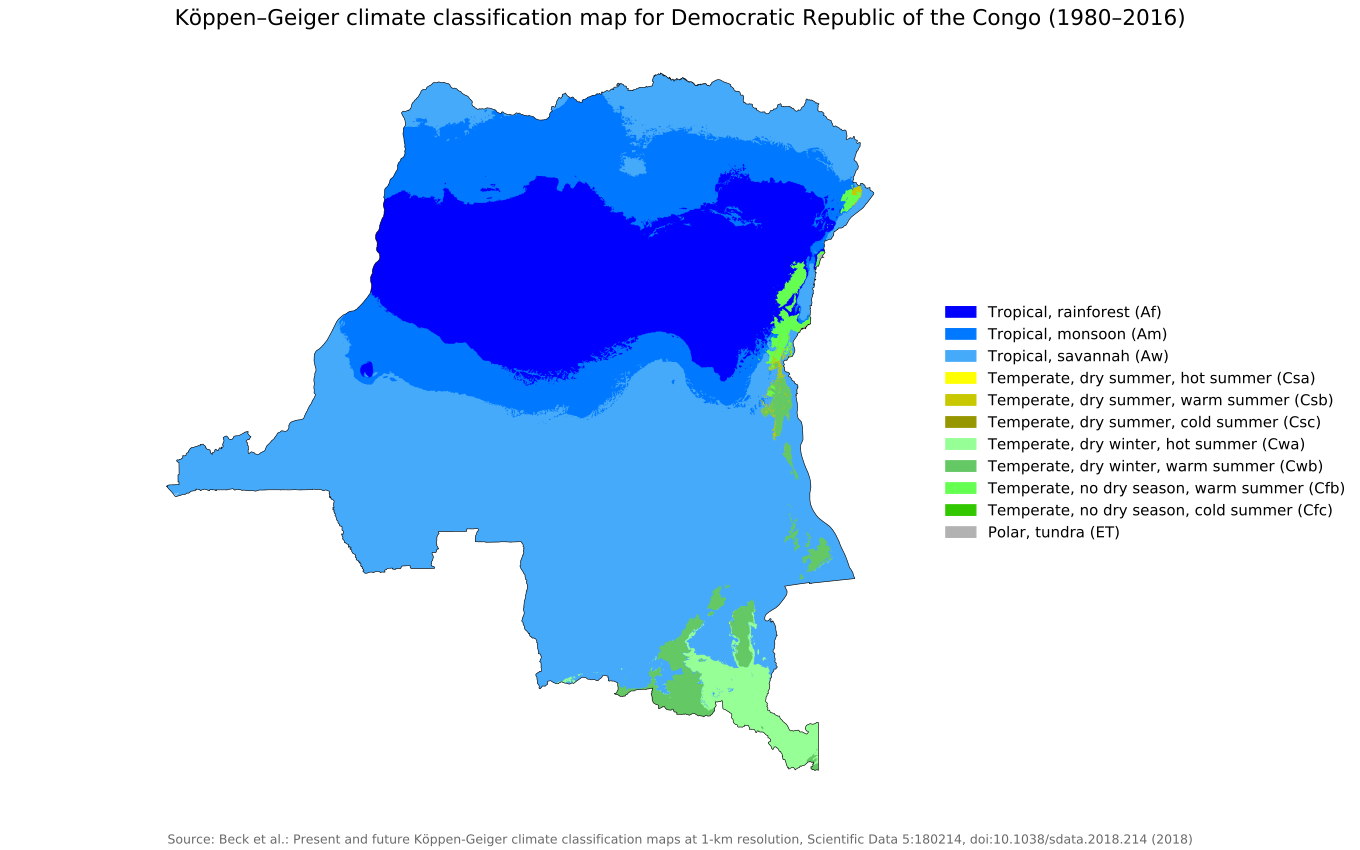
Map of Democratic Republic of Congo
Democratic Republic Congo Location Map
Democratic Republic of the Congo GDP Evolution Map
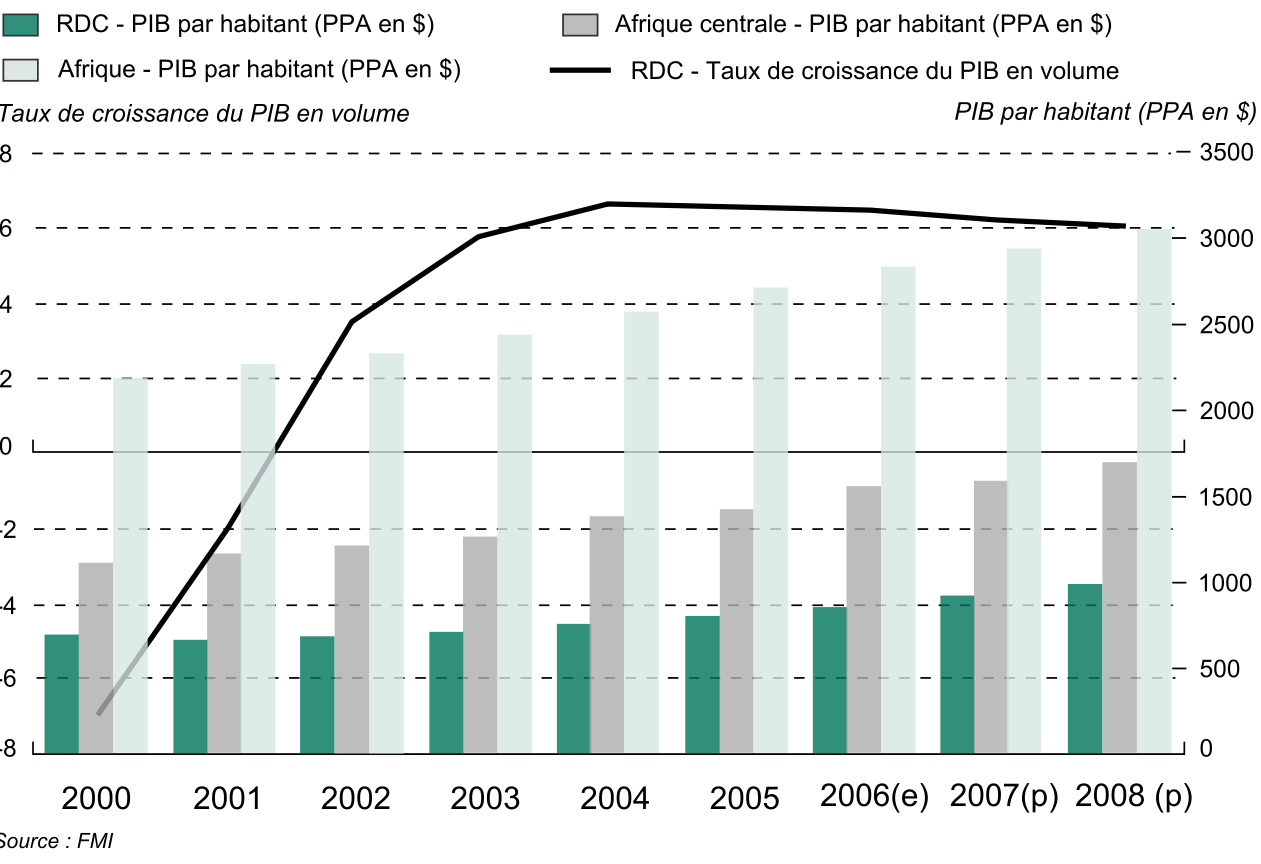 Graph comparing DRC and Central Africa GDP per capita (PPA) and growth rates.
Graph comparing DRC and Central Africa GDP per capita (PPA) and growth rates.This chart illustrates GDP per capita in purchasing power parity (PPA) in the Democratic Republic of the Congo compared to Central Africa and the overall continent from 2000 to 2008. It highlights significant economic growth trends, with a focus on the DRC's increasing GDP growth rate over the years.
Democratic Republic Congo Satellite Map
Congo transport map
Democratic Republic of Congo Earth Map
Democratic Republic Congo Train River Map
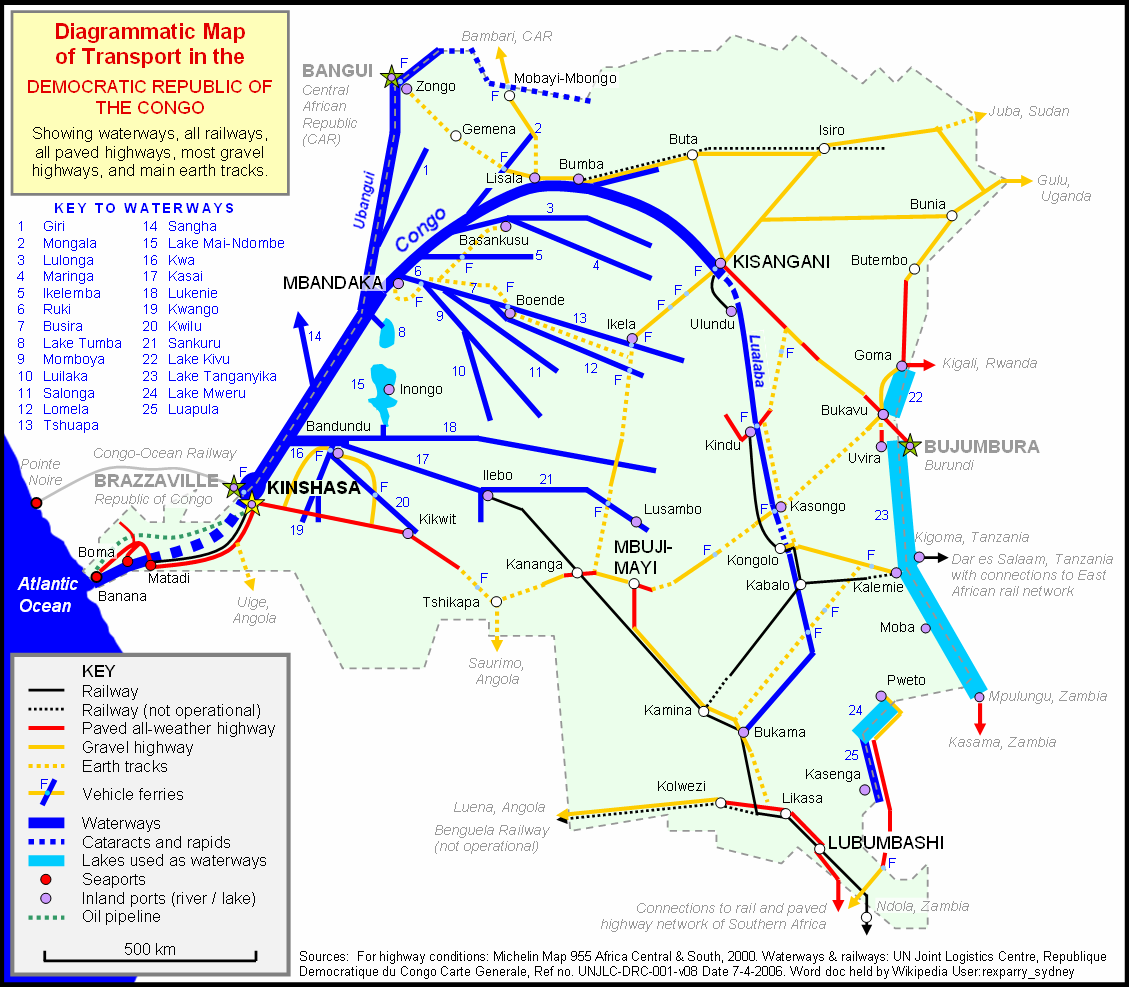
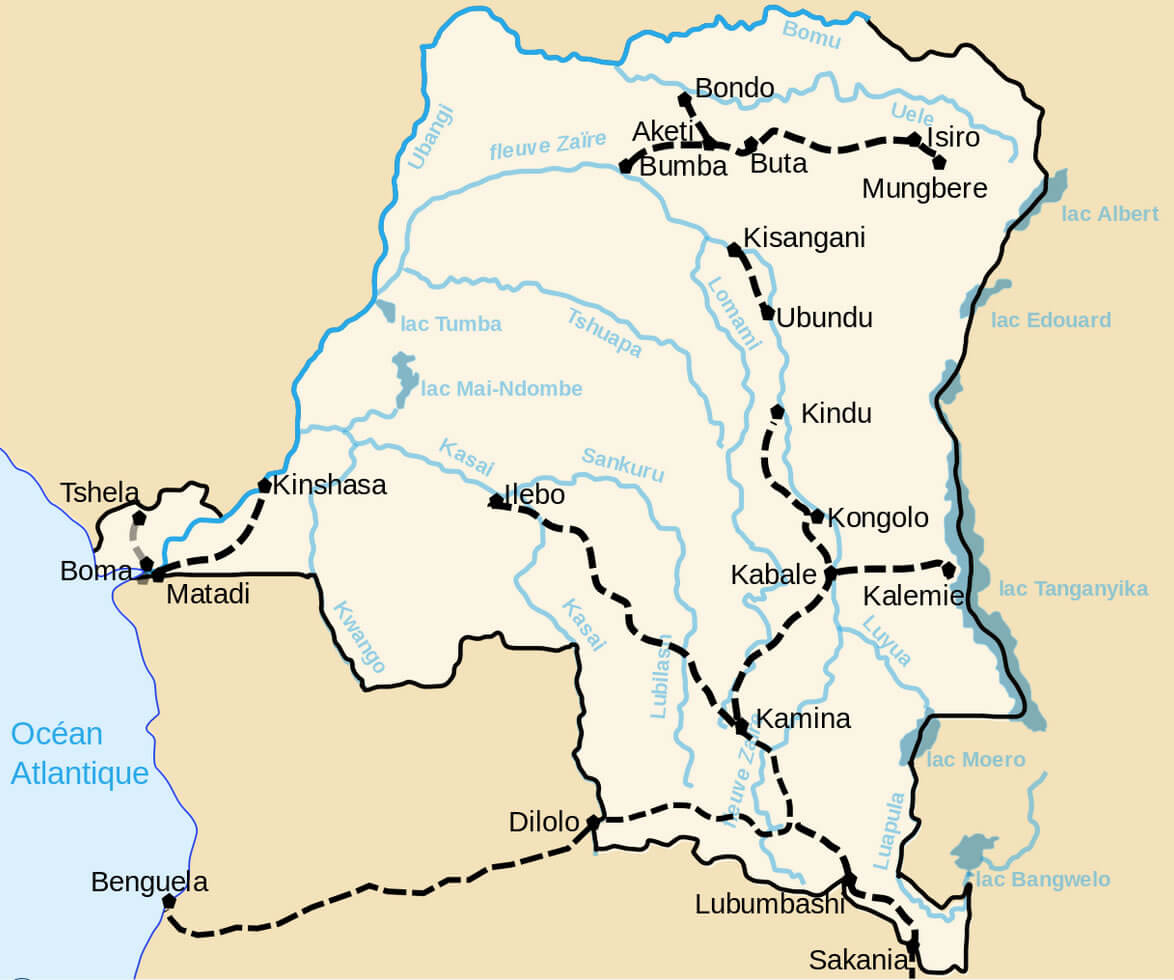 Map showing major rivers, railways, and cities in the DRC.
Map showing major rivers, railways, and cities in the DRC.This map highlights the transportation network of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, including key rivers like the Congo River and its tributaries, major railway routes, and cities such as Kinshasa, Lubumbashi, Kisangani, and Matadi. It also marks lakes such as Albert, Tanganyika, and Mai-Ndombe, illustrating the country’s reliance on waterways for transportation and trade.
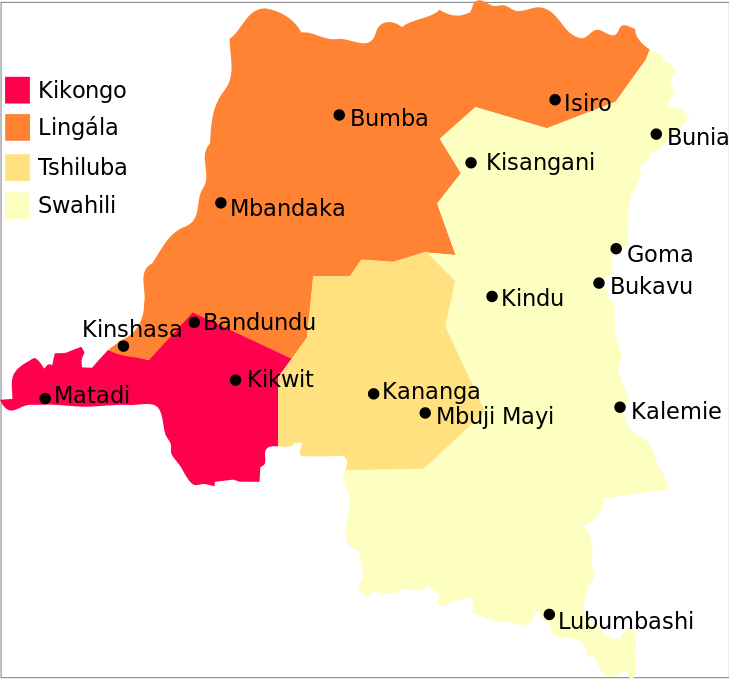
Congo Major Languages
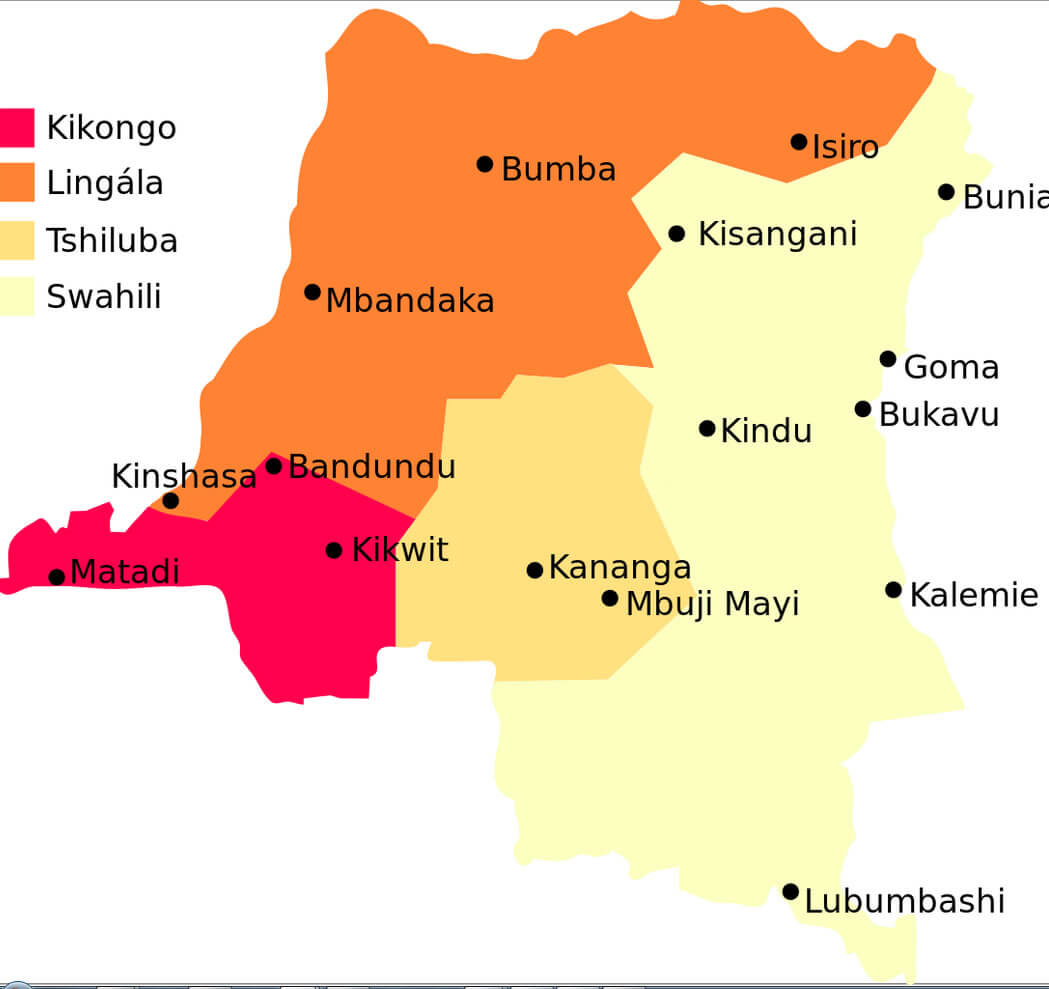 Map showing Kikongo, Lingala, Tshiluba, and Swahili regions in the DRC.
Map showing Kikongo, Lingala, Tshiluba, and Swahili regions in the DRC.This map highlights the primary languages spoken across the Democratic Republic of the Congo: Kikongo in the west, Lingala in the north and central areas, Tshiluba in the south-central regions, and Swahili in the eastern part of the country. Major cities like Kinshasa, Lubumbashi, and Kisangani are also marked.
Map of Democratic Republic Congo Africa
Map of Democratic Republic Congo World
Congo cities map
Congo map
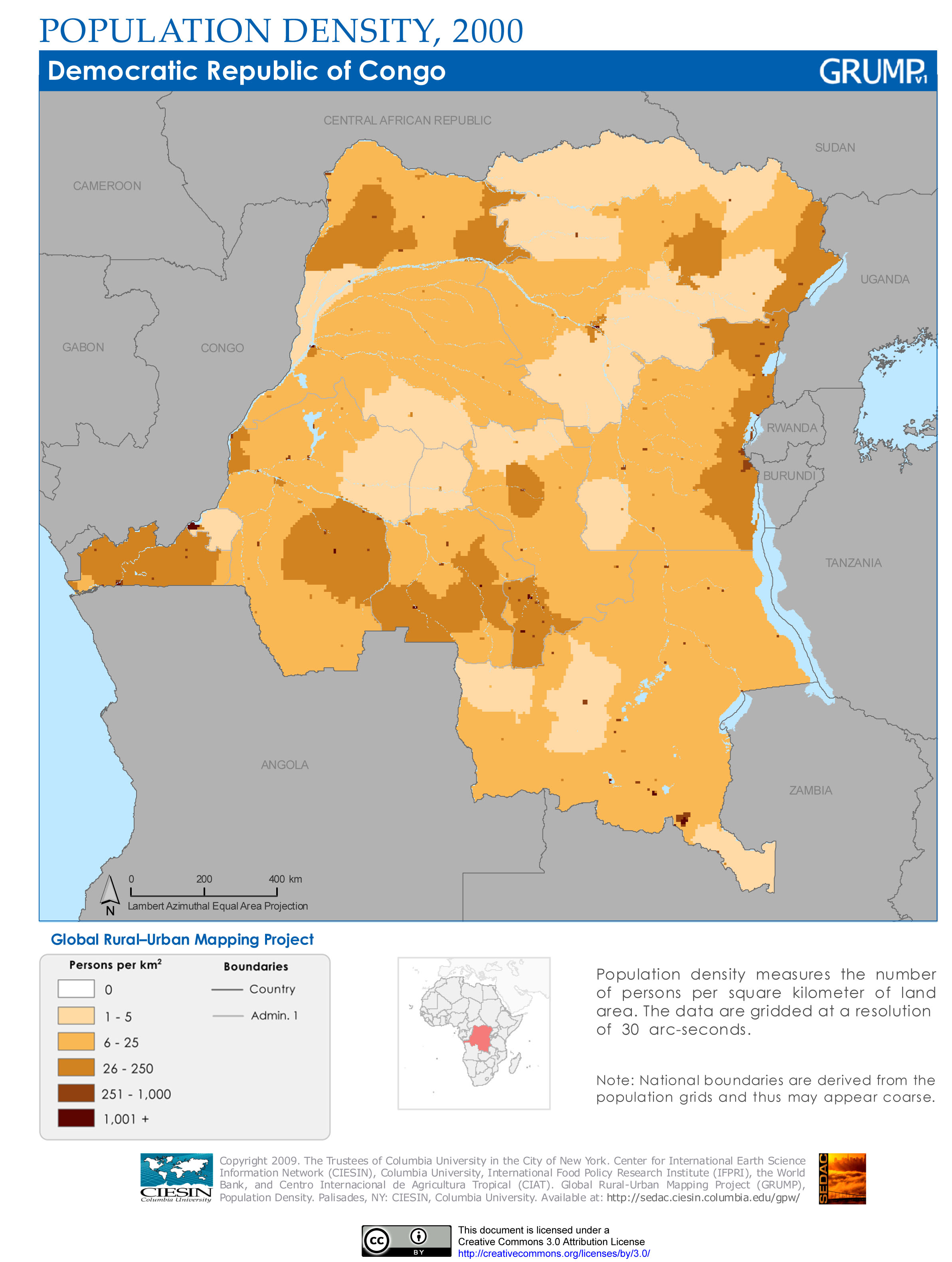
Congo population map
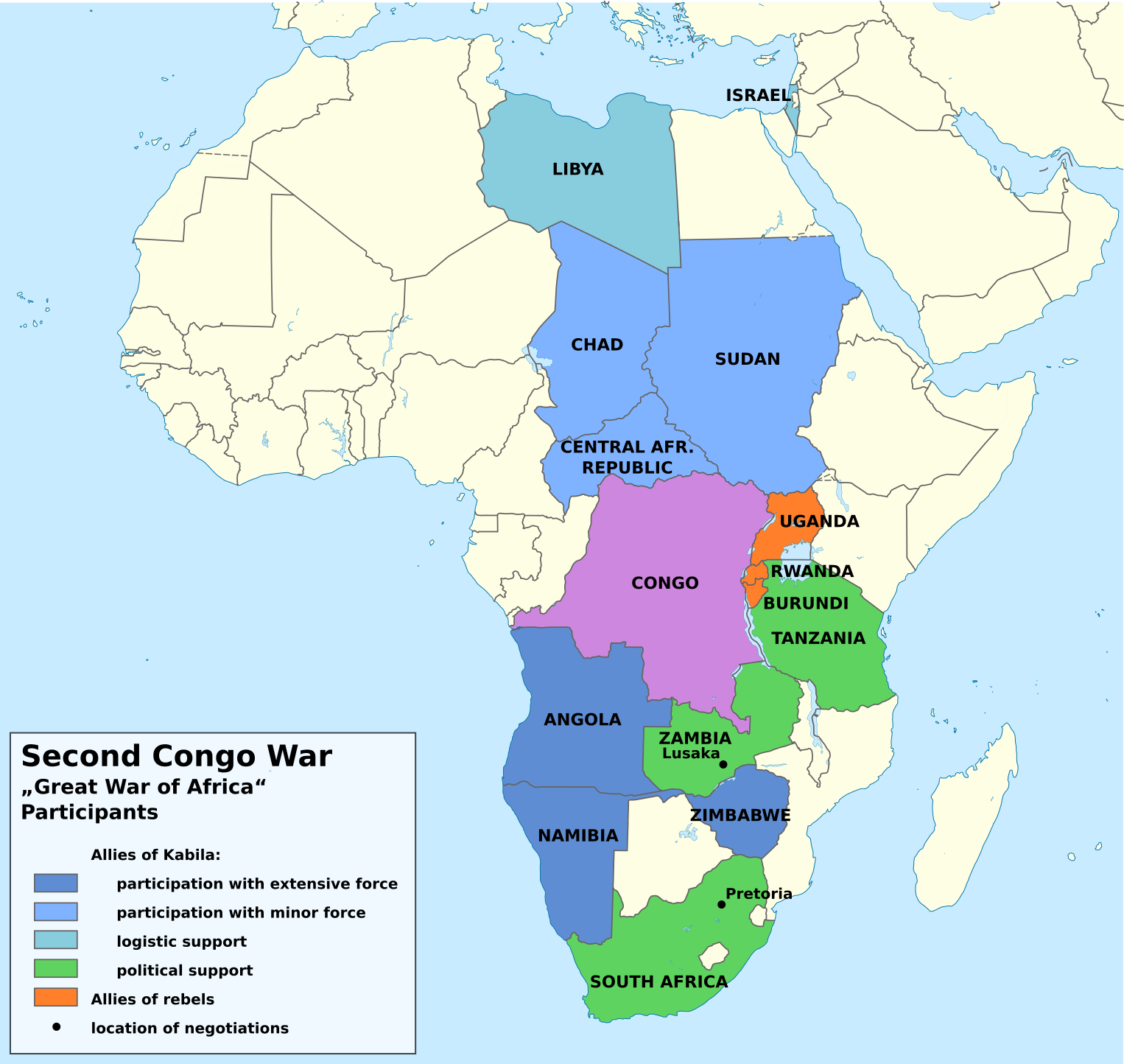
Second Congo War Africa Map
Feel free to explore these pages as well:
- Head of Performance Marketing
- Head of SEO
- Linkedin Profile: linkedin.com/in/arifcagrici
