Printable Ethiopia Map: Political, Physical, Regions, and Cities Maps
Ethiopia is a landlocked country in the Horn of Africa, situated in eastern Africa. It borders Eritrea to the north, Djibouti and Somalia to the east, Kenya to the south, and Sudan and South Sudan to the west. Located close to the Arabian Peninsula, Ethiopia's strategic position makes it influential in regional trade and geopolitics.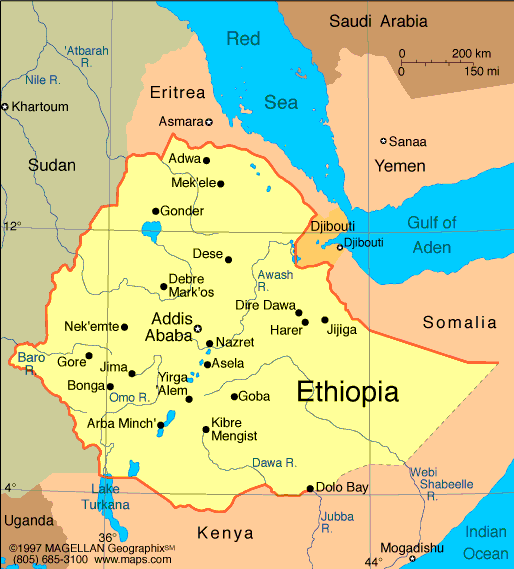
Ethiopia major cities map
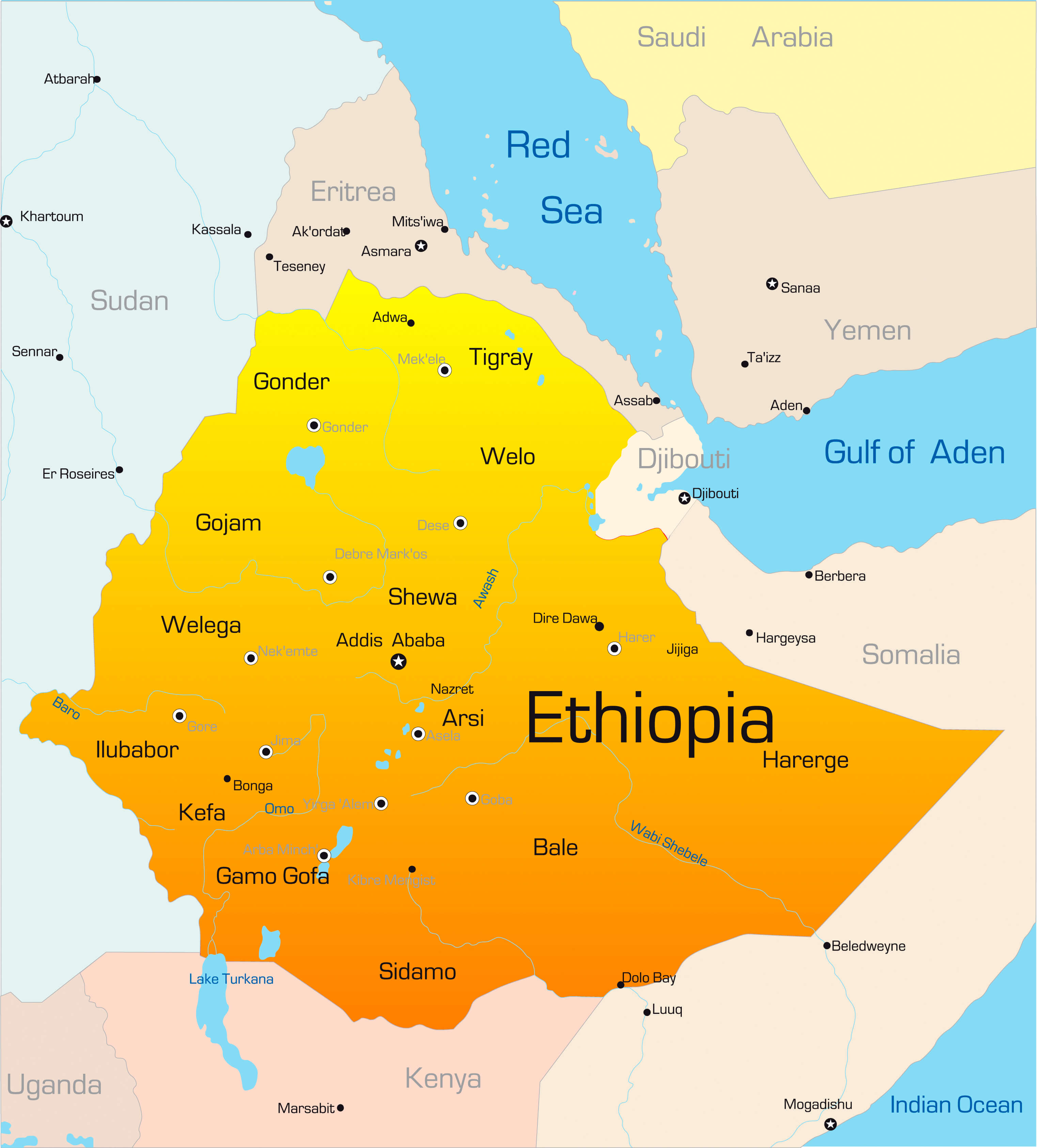
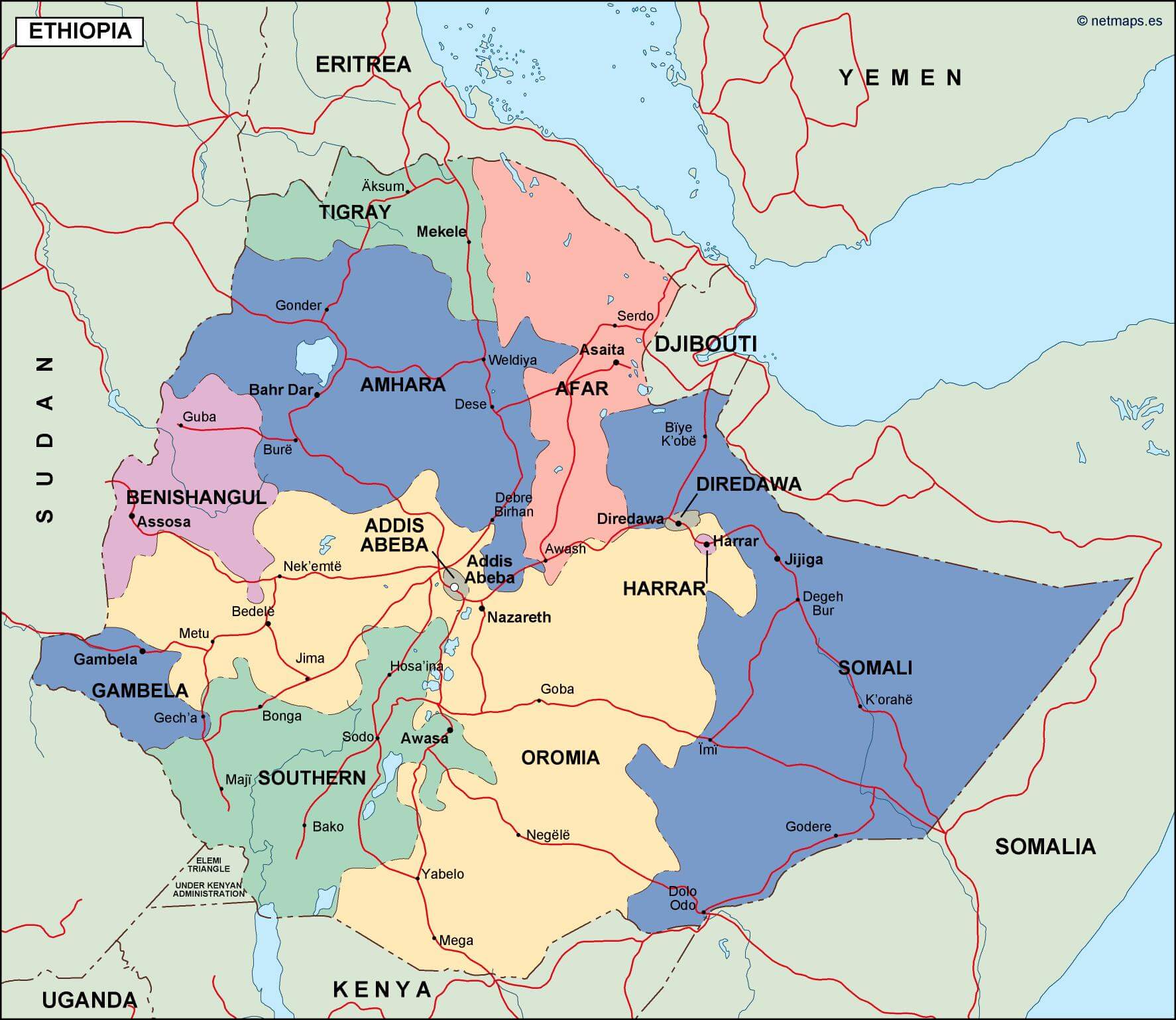
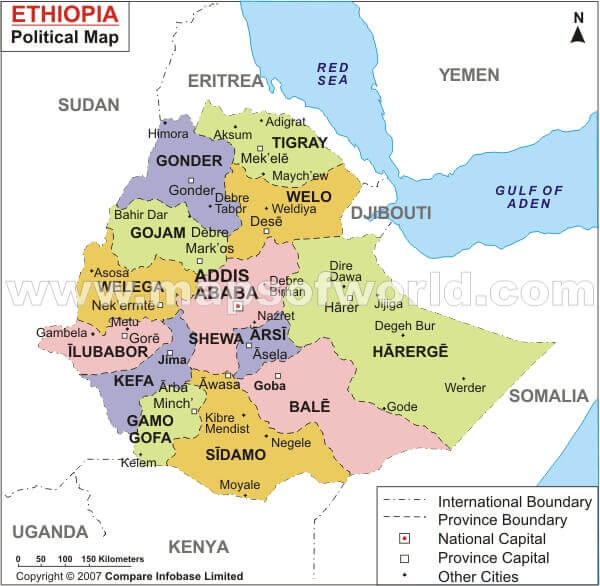
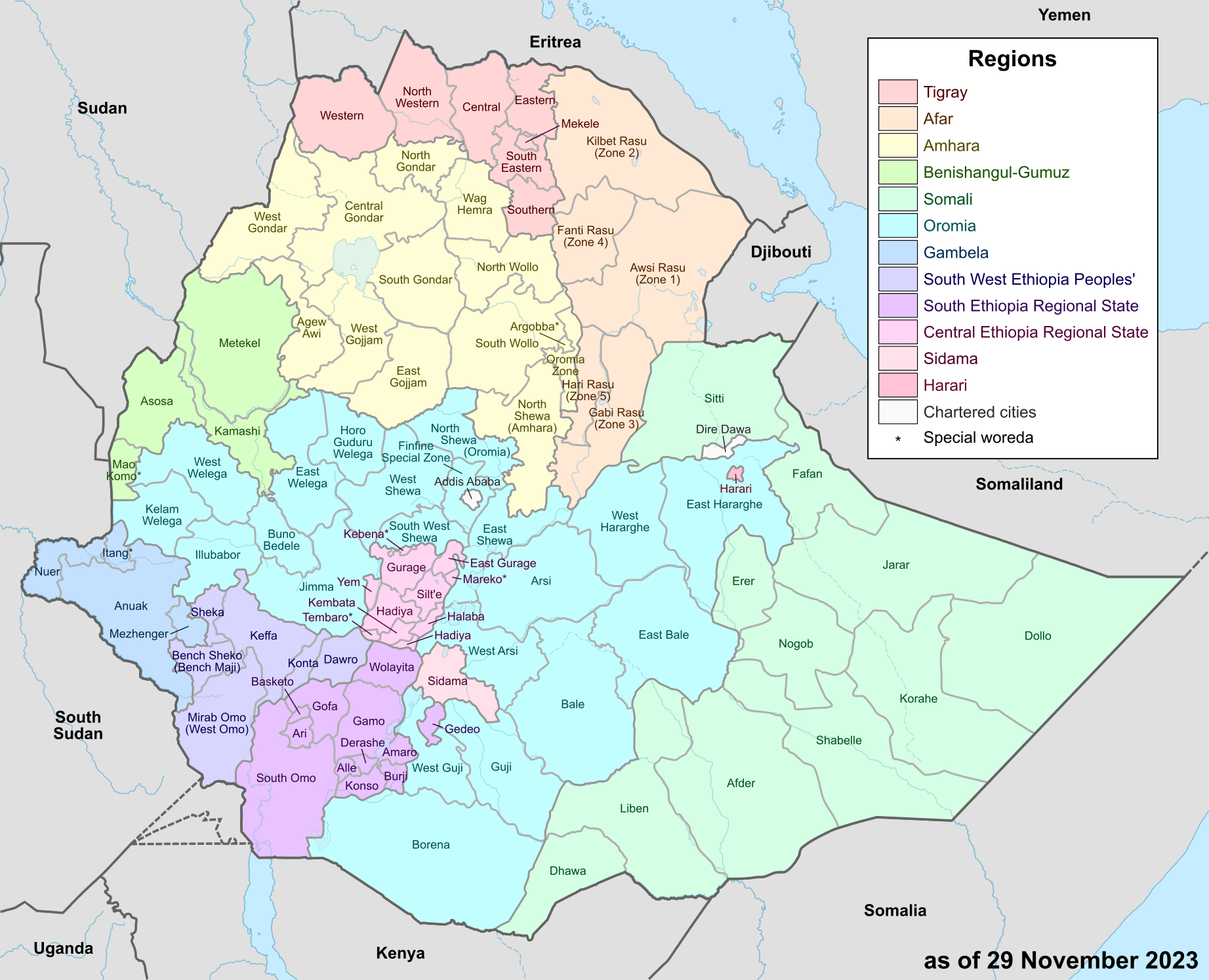
Ethiopia administrative map
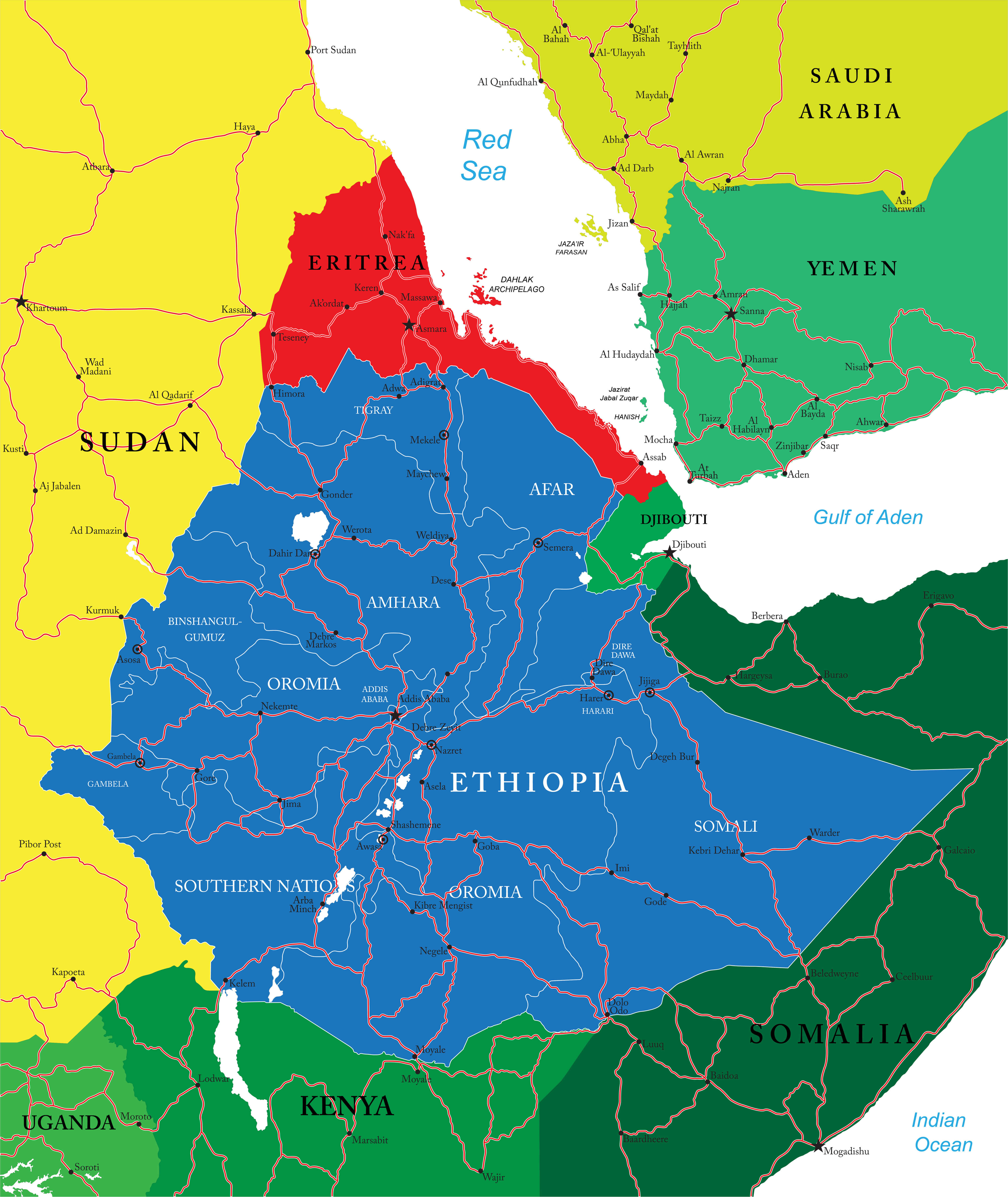
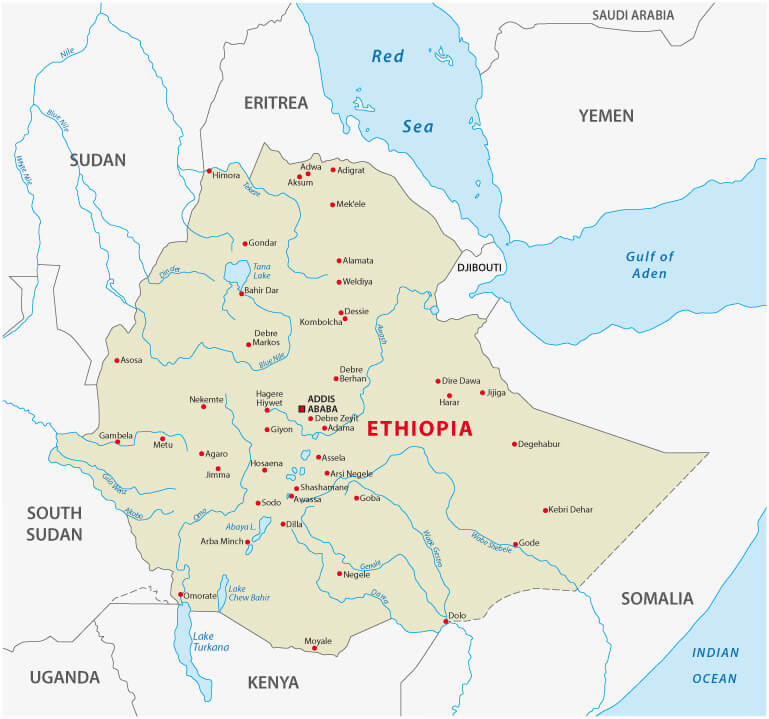
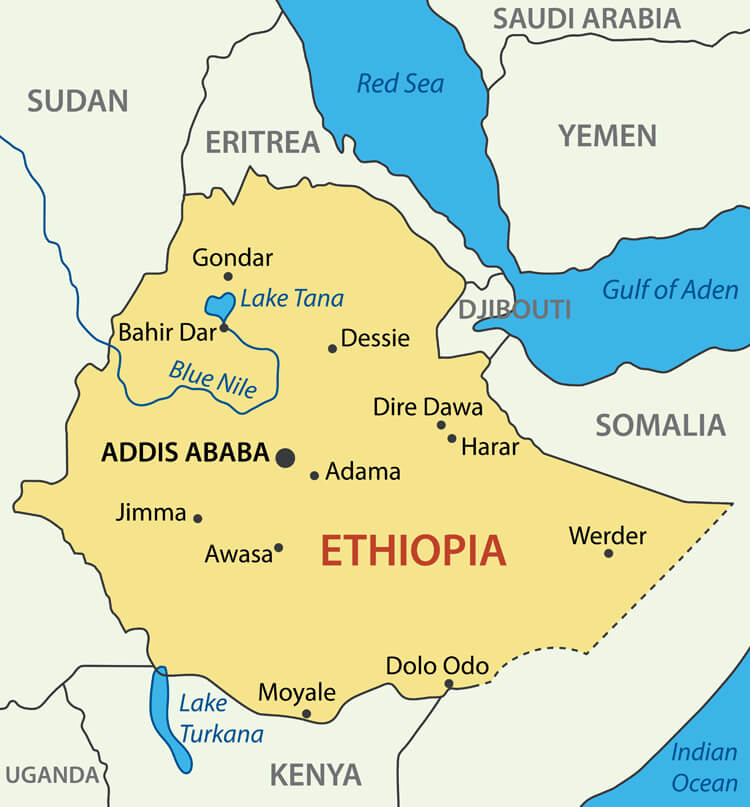
Map of Ethiopia — Political & Physical Overview
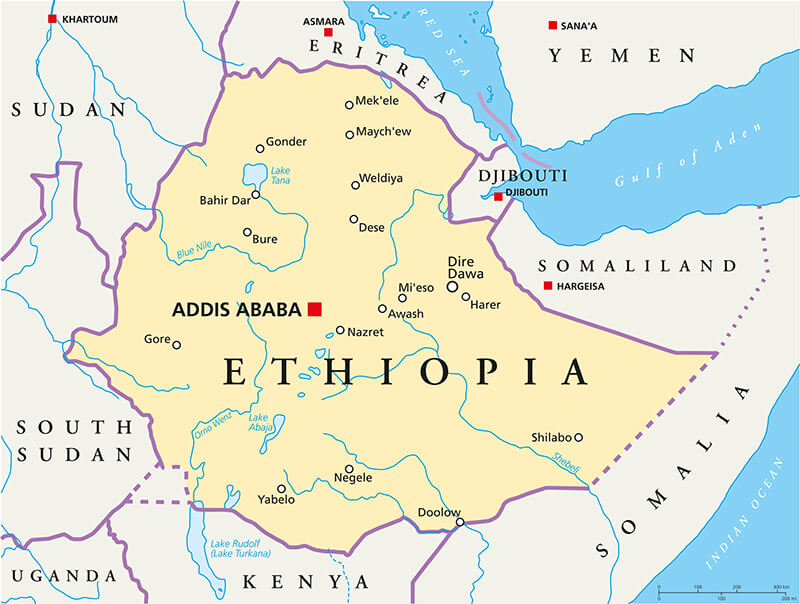
 Map of Ethiopia showing borders, major cities, lakes, rivers and neighboring countries.
Map of Ethiopia showing borders, major cities, lakes, rivers and neighboring countries.This map of Ethiopia shows political boundaries, major cities (including Addis Ababa), principal lakes and rivers (Lake Tana, the Blue Nile), and elevation changes from highlands to lowlands. It also highlights neighboring countries—Eritrea, Djibouti, Somalia, Kenya, South Sudan and Sudan—placing Ethiopia in the Horn of Africa.
Brief information about Ethiopia
Located in the Horn of Africa, Ethiopia is one of the world's oldest nations with a rich history dating back thousands of years. Known as the cradle of humanity, Ethiopia is where the famous "Lucy" fossil was discovered, providing crucial evidence of early human origins. The country has a unique heritage as one of the few nations to successfully resist colonisation and played a pivotal role in African independence movements. The capital, Addis Ababa, is also the headquarters of the African Union, cementing Ethiopia's status as a key player in the continent's political landscape.
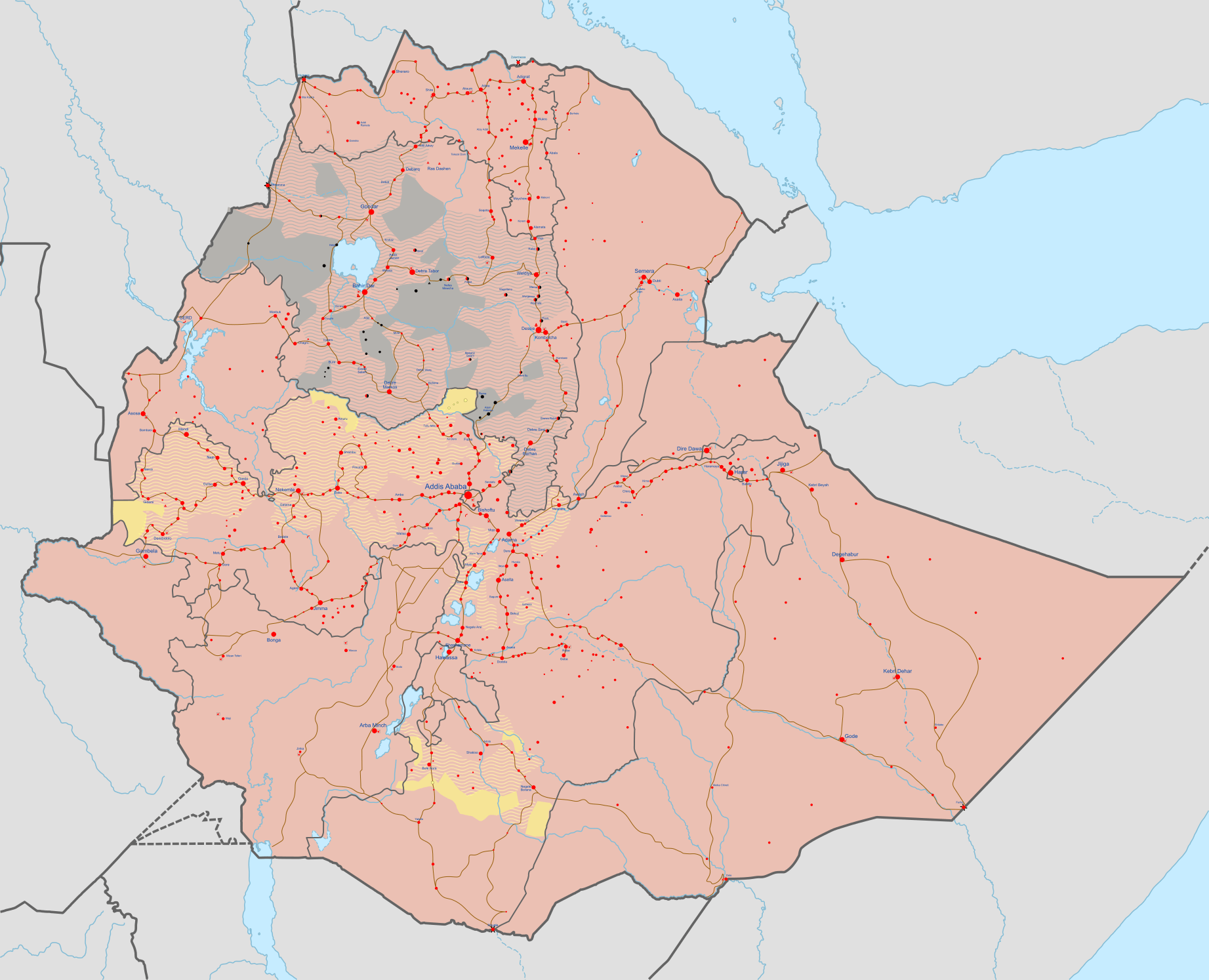
Ethiopia rivers and cities map
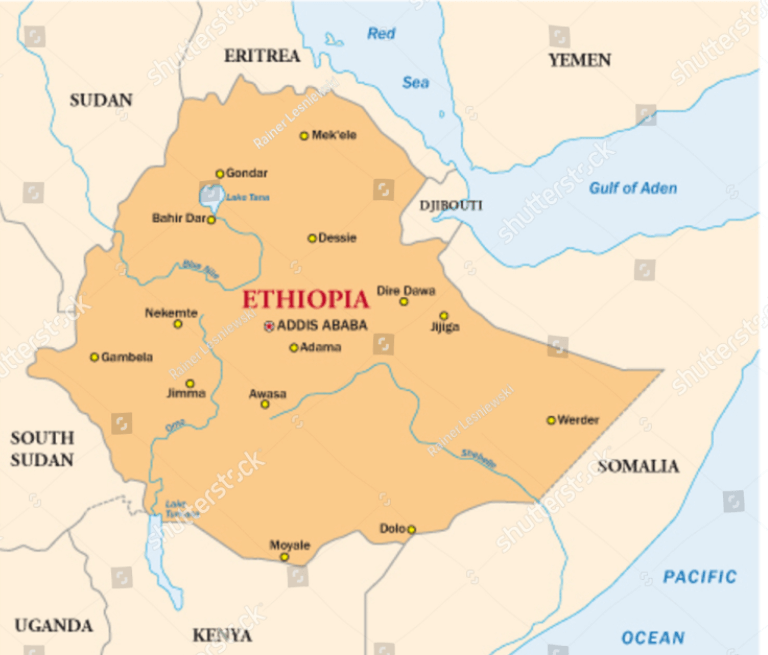
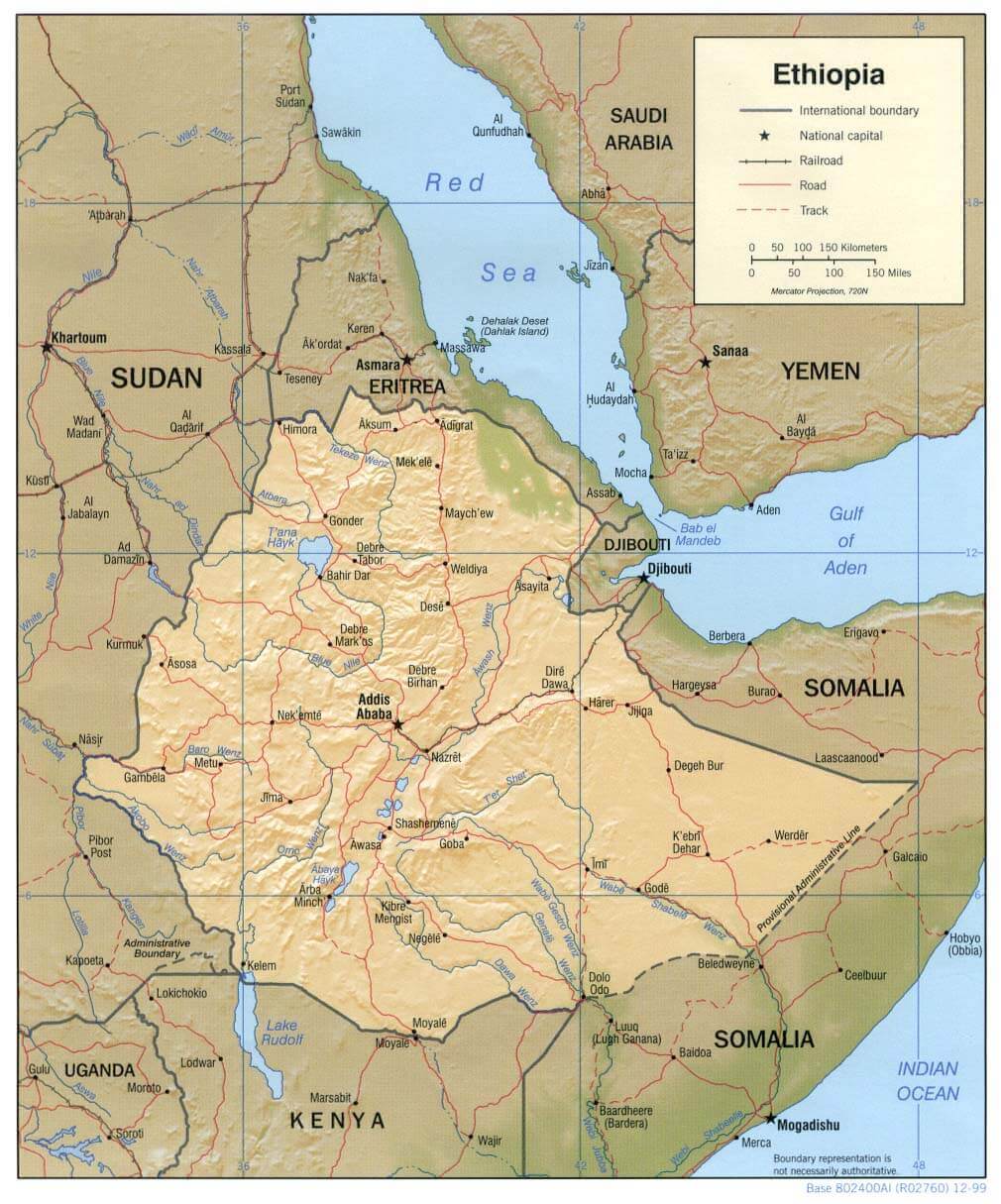
Ethiopia road map
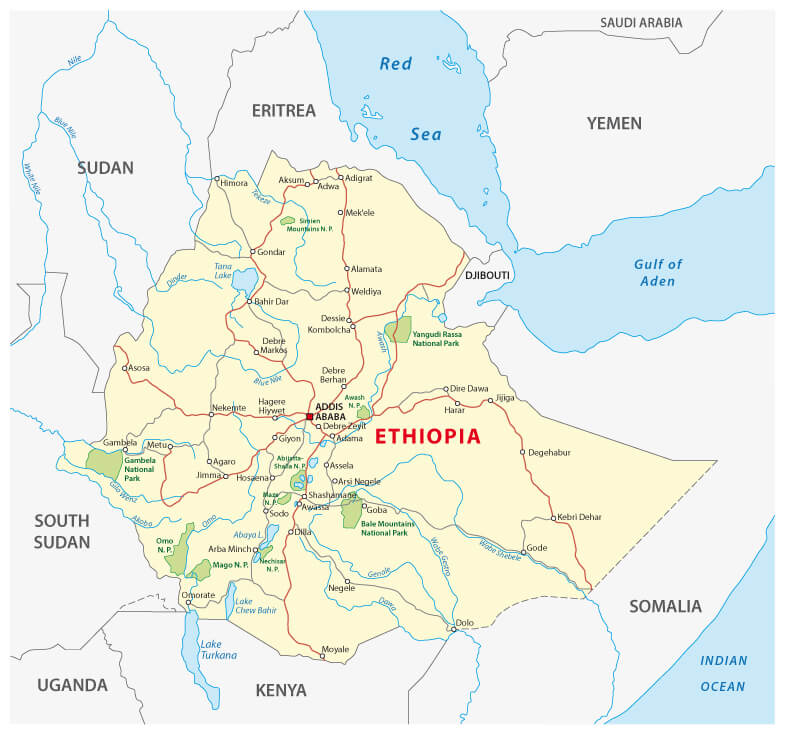
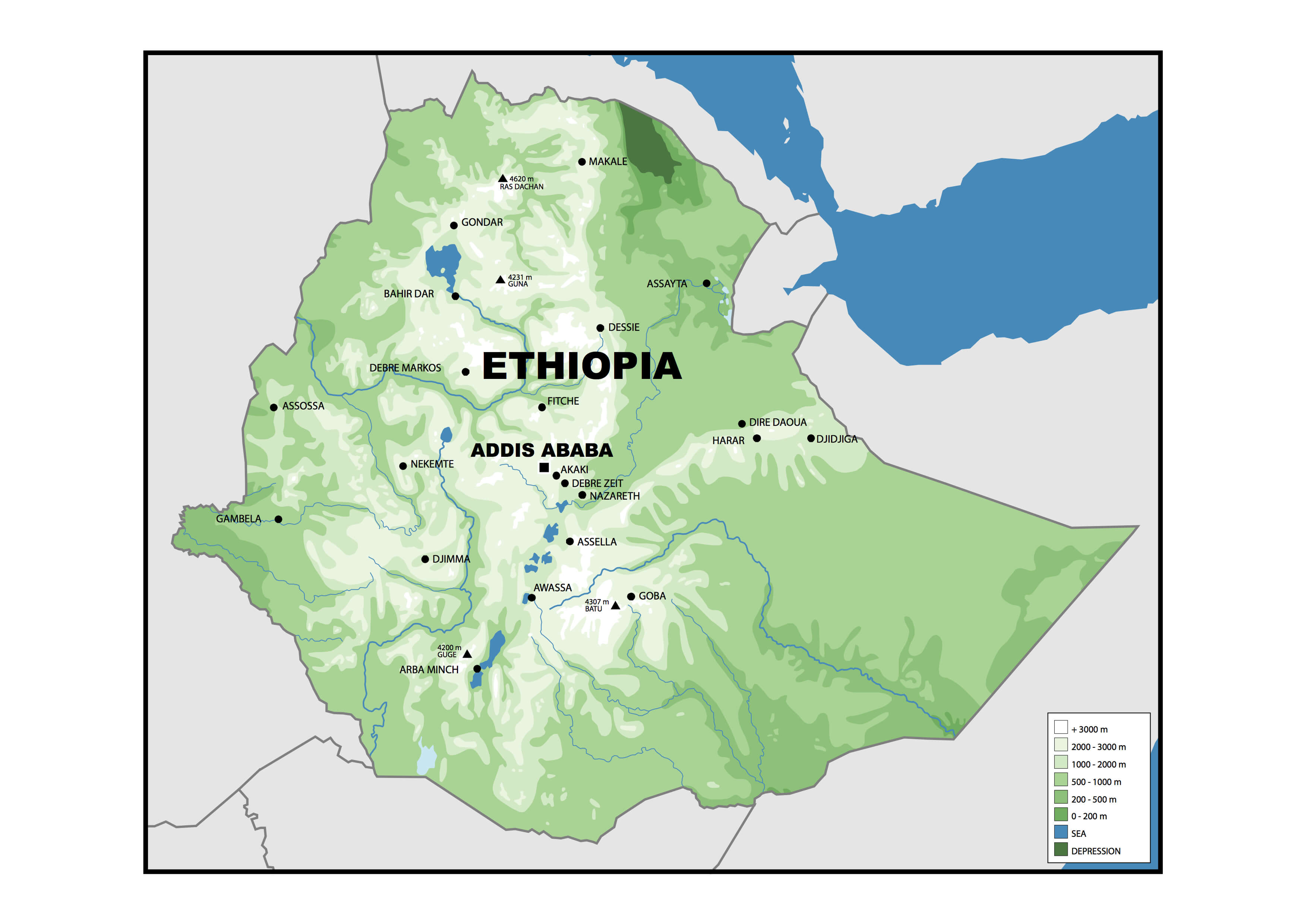
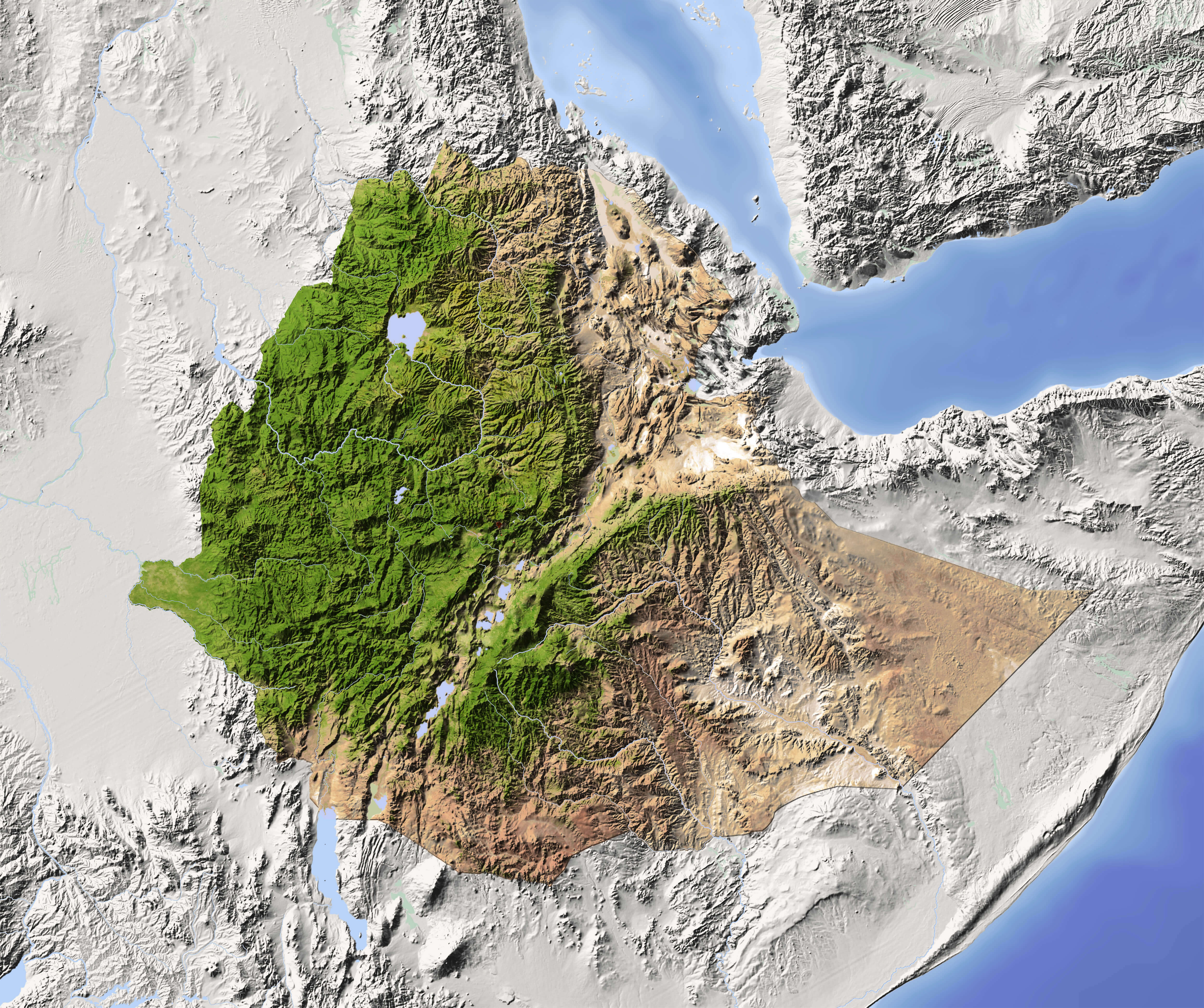
Ethiopia physical map
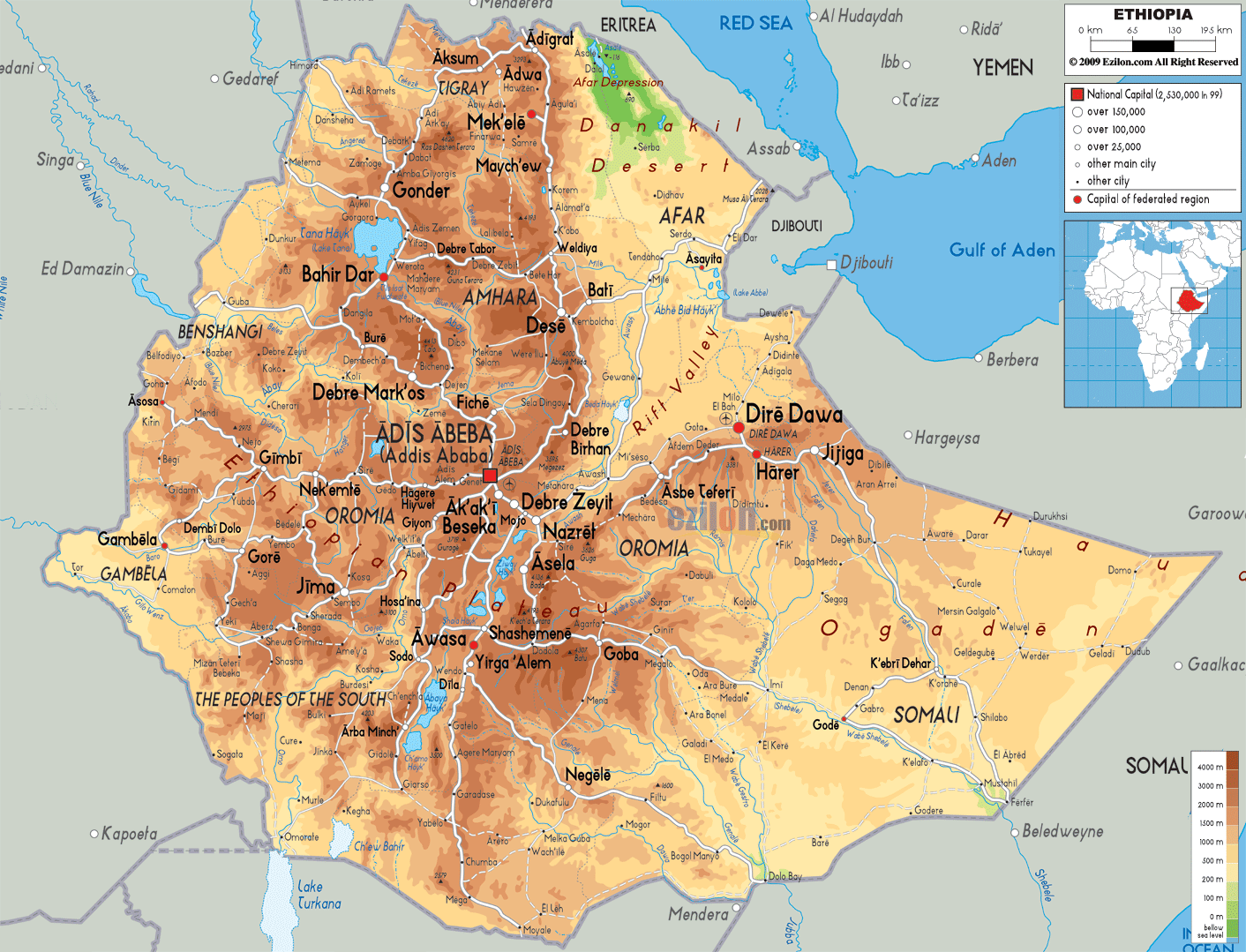
Ethiopia's diverse geography includes towering mountains, vast plateaus and the Great Rift Valley, home to some of Africa's most breathtaking scenery. The country is home to over 80 ethnic groups and languages, reflecting a vibrant cultural mosaic. It is also famous for its ancient traditions, such as the Ethiopian Orthodox Church and its unique calendar system. In addition, Ethiopia is known as the birthplace of coffee, a key part of its culture and economy. Despite challenges such as poverty and drought, the country is making strides in development and infrastructure.
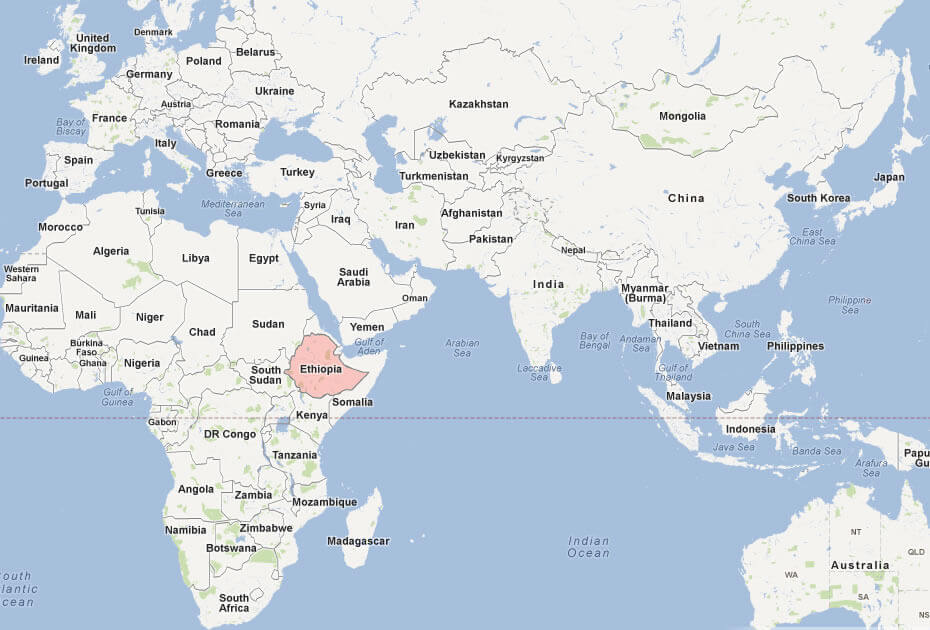
Where is located Ethiopia on the World and Africa Map?
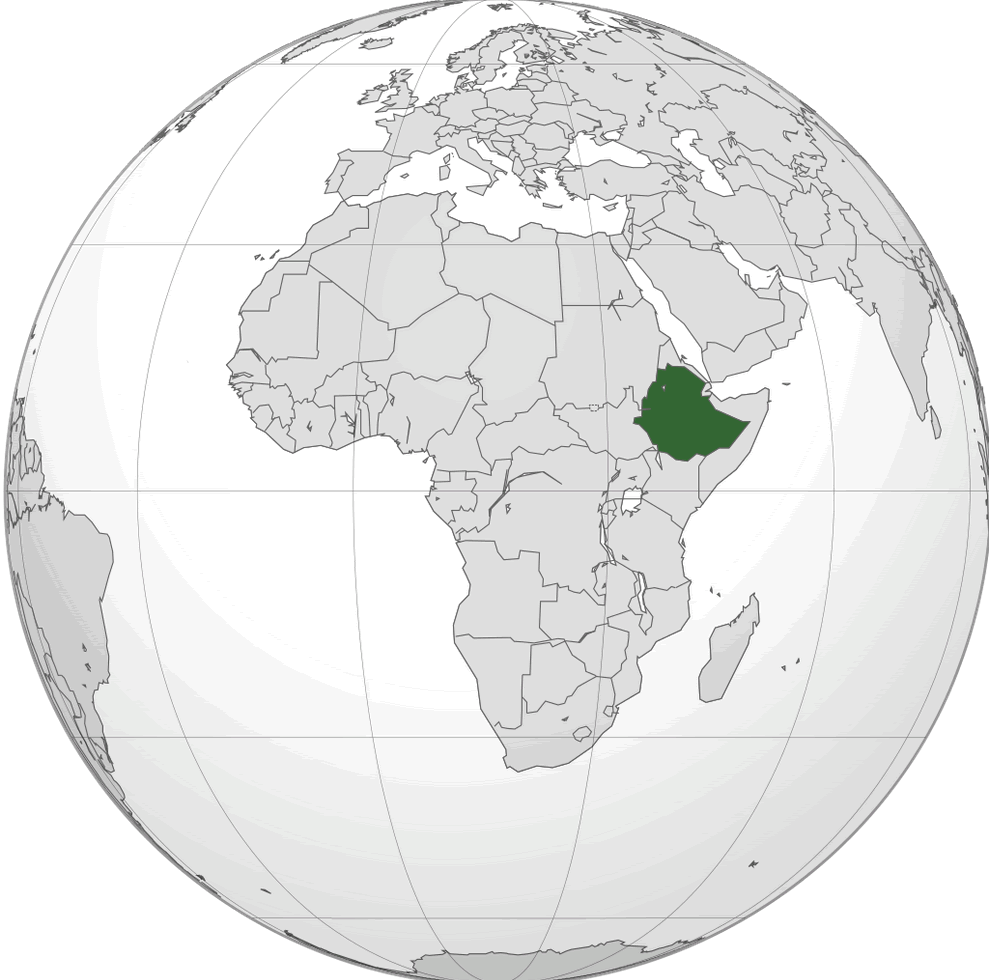 Where is located Ethiopia on the World Map
Where is located Ethiopia on the World MapEthiopia is located in the Horn of Africa, in the eastern part of the African continent. It is a landlocked country bordered by Eritrea to the north, Djibouti and Somalia to the east, Kenya to the south and Sudan and South Sudan to the west. Its strategic location places it close to the Arabian Peninsula, making it a key player in regional geopolitics and trade routes.
Ethiopia location map in the World and Africa
The country lies within the Great Rift Valley, a geological wonder that runs through East Africa, giving Ethiopia a diverse landscape of rugged mountains, high plateaus and deep valleys. Ethiopia's location makes it one of the most ecologically diverse countries in Africa, with climates ranging from arid lowlands to fertile highlands. The Blue Nile, one of the main tributaries of the Nile, rises from Lake Tana in the Ethiopian highlands, underlining its geographical importance.
Ethiopia cities and Addis Ababa map
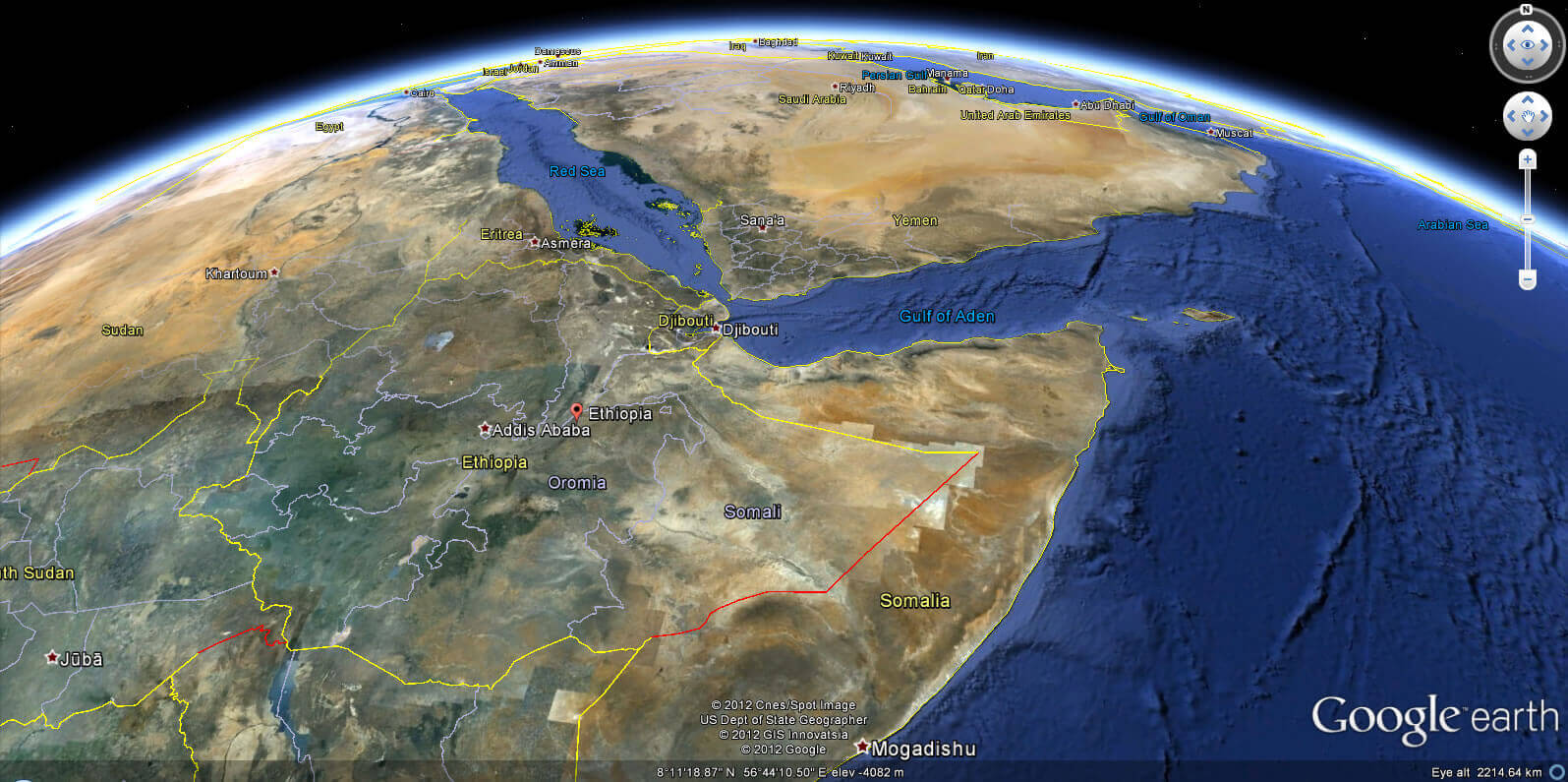
Ethiopia's location has historically positioned it as a bridge between Africa and the Middle East, fostering trade, cultural exchange and religious diversity. Its proximity to the Red Sea and the Gulf of Aden adds to its geopolitical importance. This strategic location has played a crucial role in Ethiopia's history, including its ancient ties to the Aksumite Empire and its influence in modern regional dynamics.
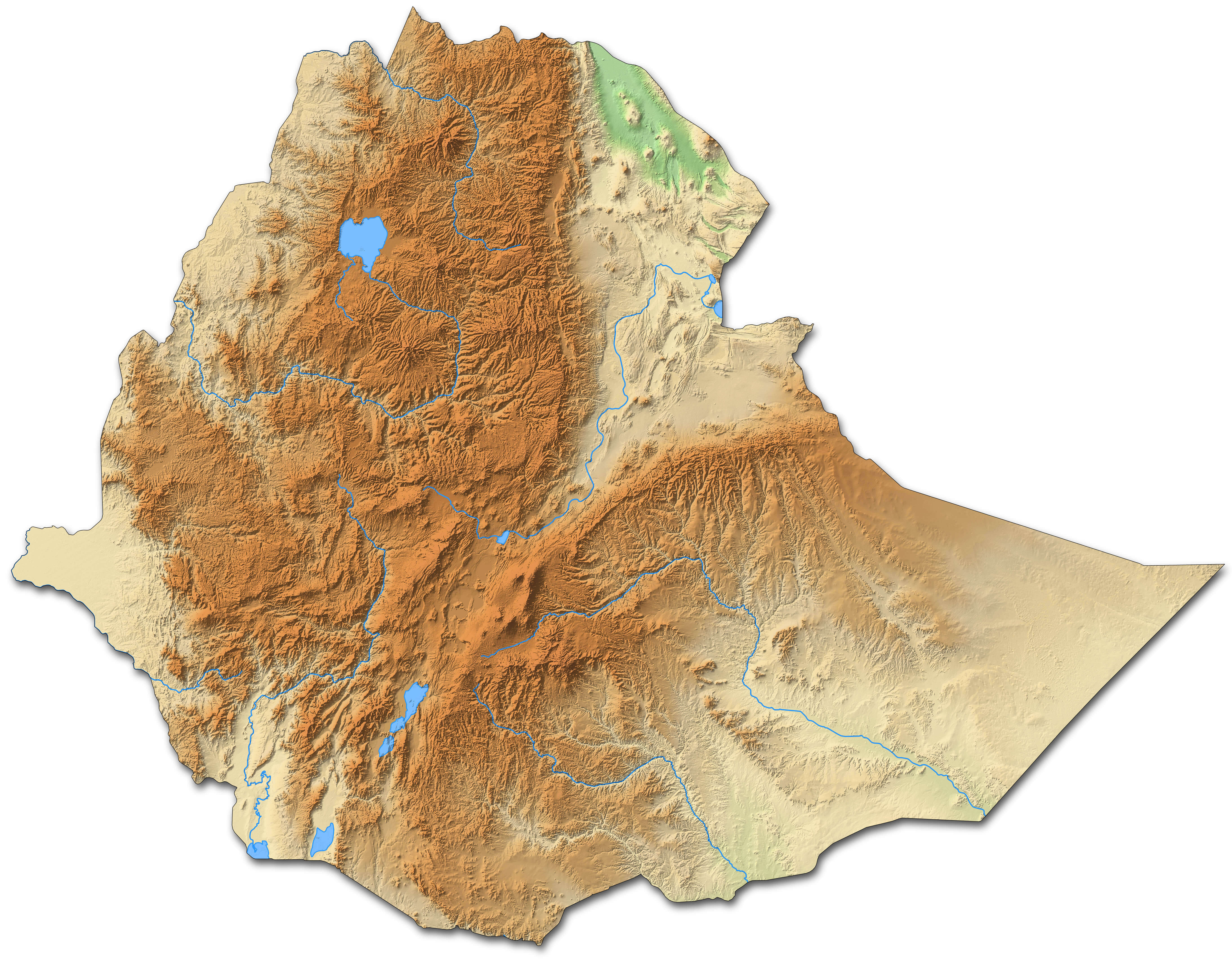
Ethiopia relief location map
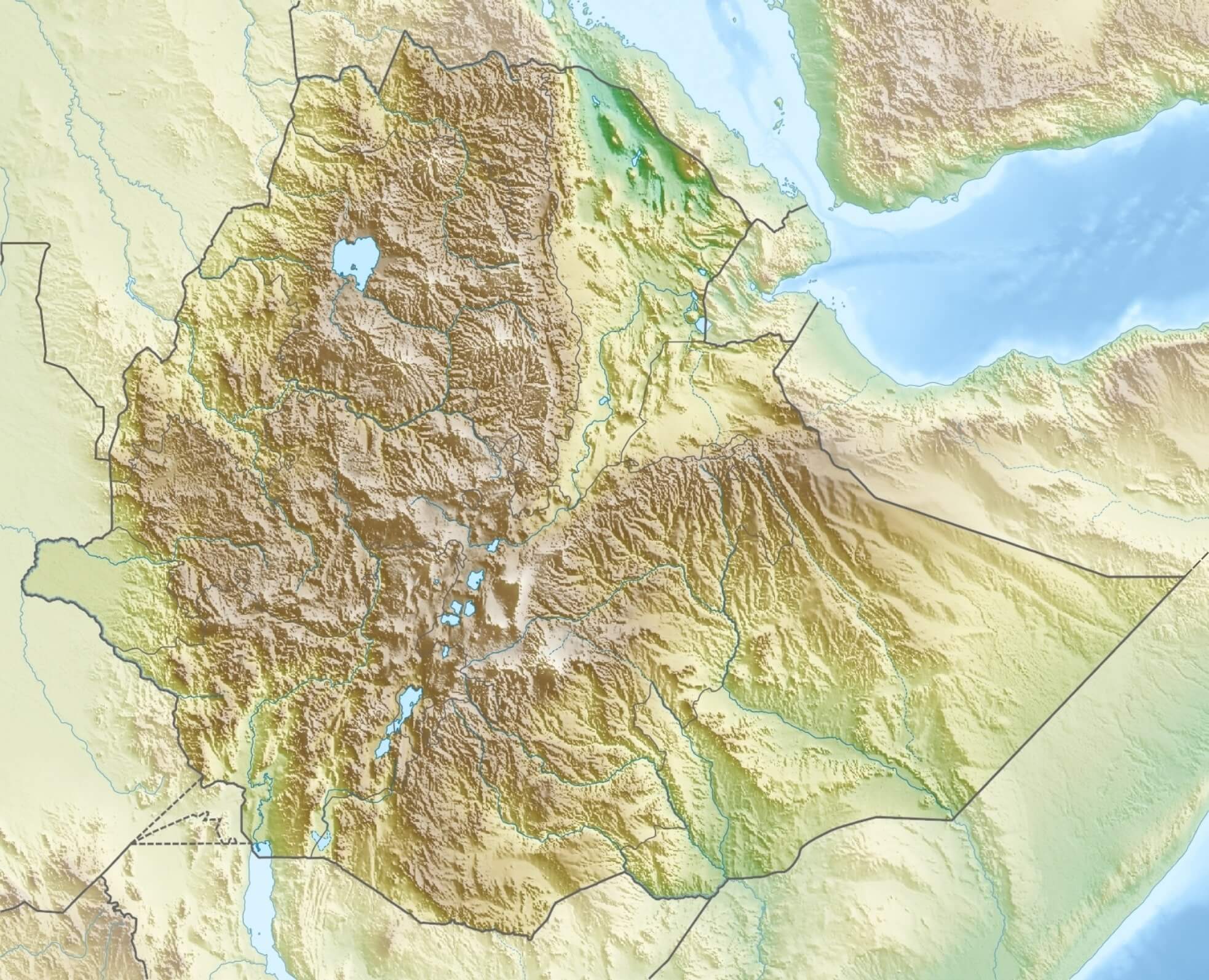
Ethiopia relief map
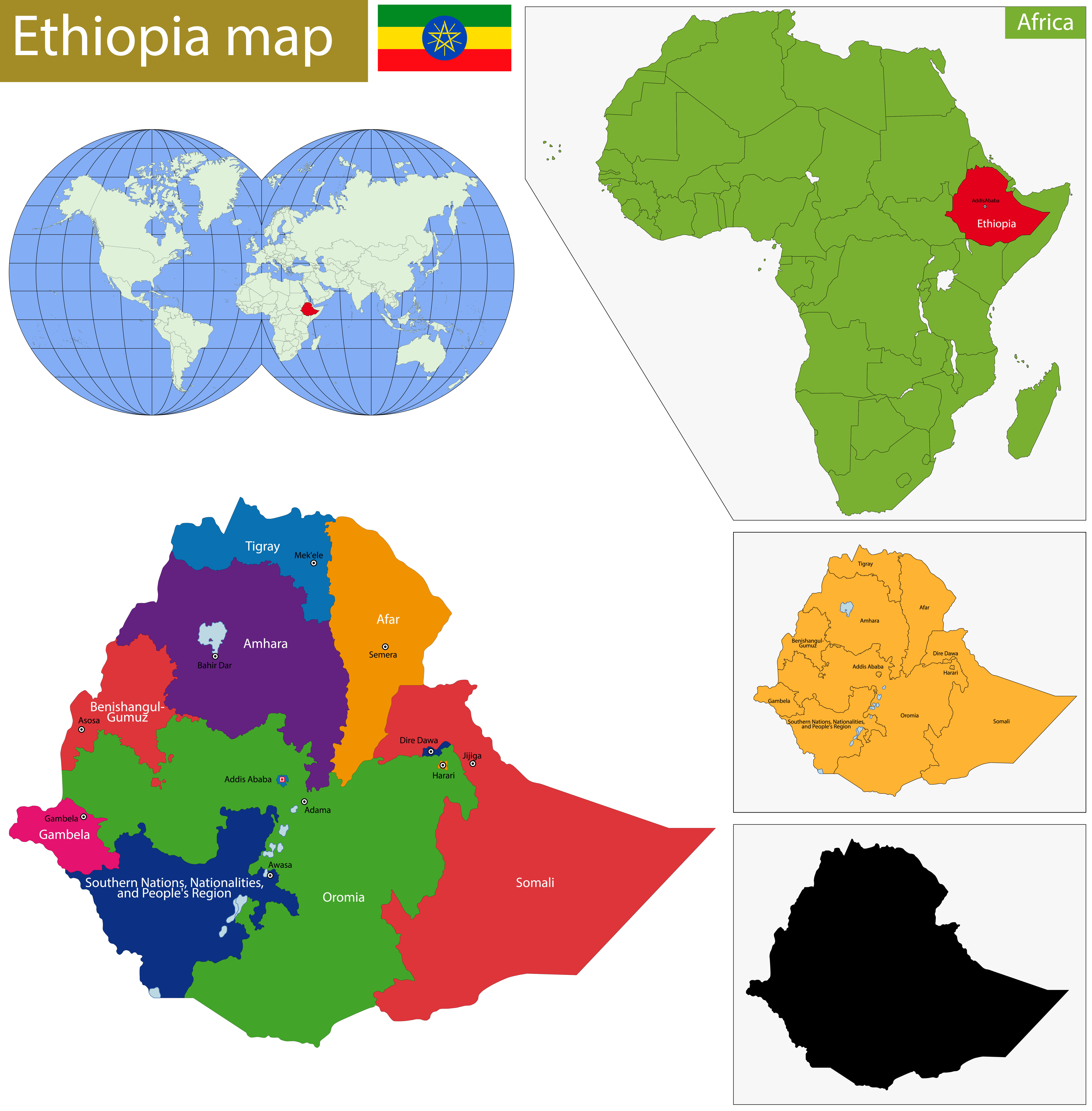
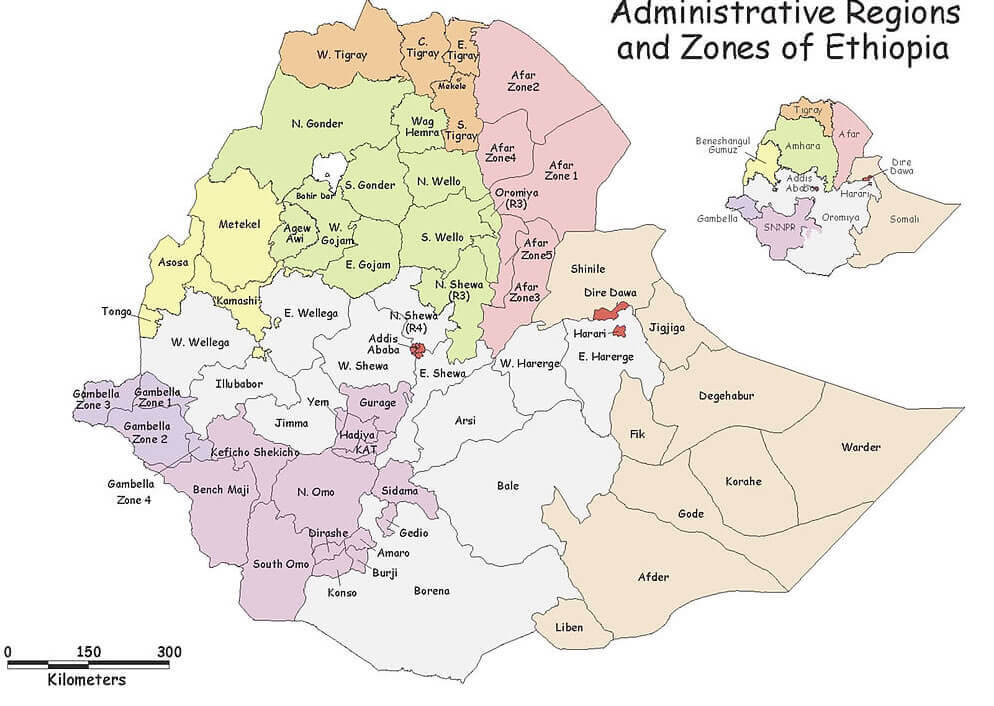
Administrative zones map of Ethiopia
Ethiopia blank map regions
Ethiopia cities map
Here are some statistical information about Ethiopia:
 Area: 1,104,300 km2 (426,400 sq mi)
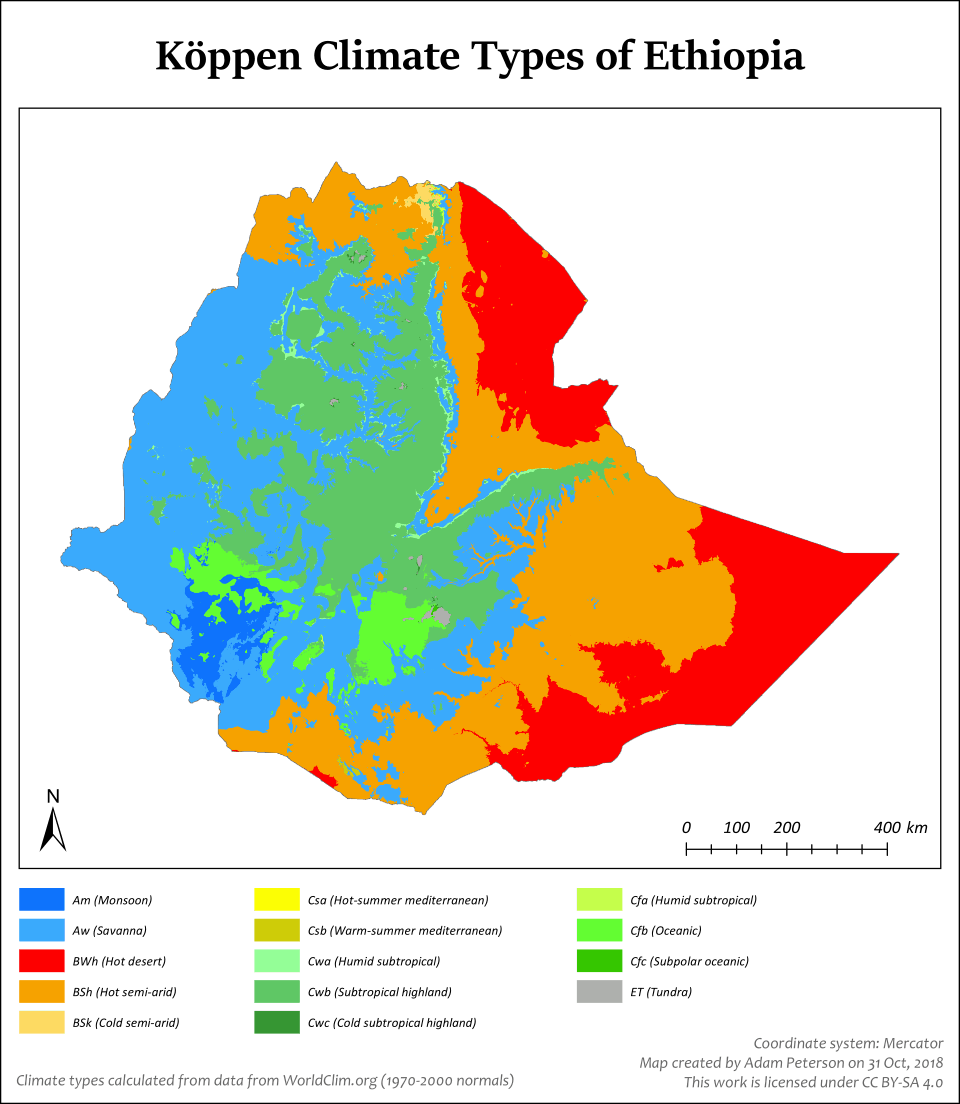
Area: 1,104,300 km2 (426,400 sq mi) Koppen climate map of Ethiopia
Map of Ethiopia Africa
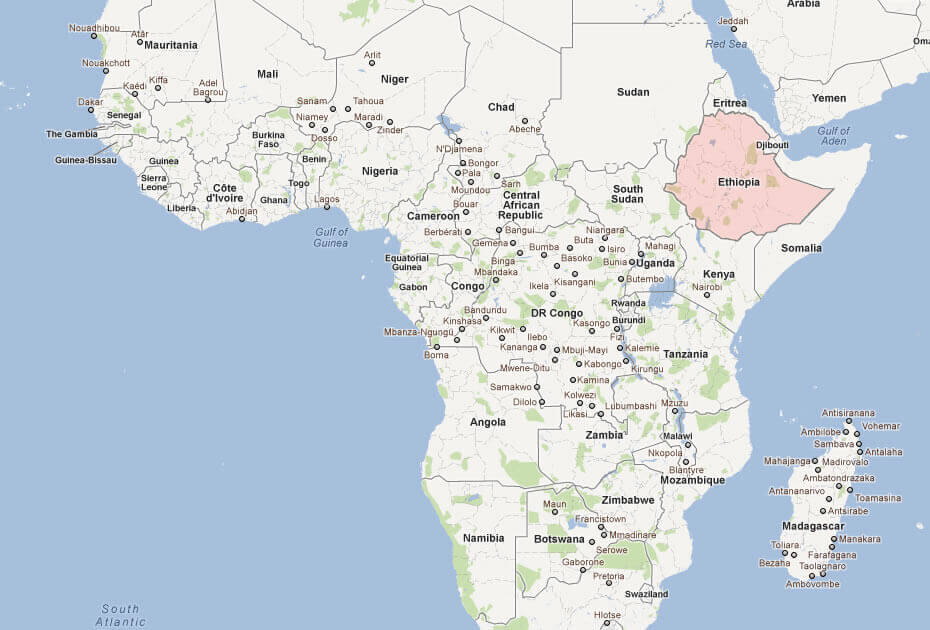
Map of Ethiopia World
Where is Ethiopia on the World map
 Religion: 67.3% Christianity (43.8% Ethiopian Orthodoxy, 22.8% P'ent'ay, 0.7% other Christian), 31.3% Islam, 0.6% traditional faiths, 0.8% others/none.
Religion: 67.3% Christianity (43.8% Ethiopian Orthodoxy, 22.8% P'ent'ay, 0.7% other Christian), 31.3% Islam, 0.6% traditional faiths, 0.8% others/none. Ethiopia country map
Ethiopia Earth map
Ethiopia lakes national park and rivers map
Ethiopia map
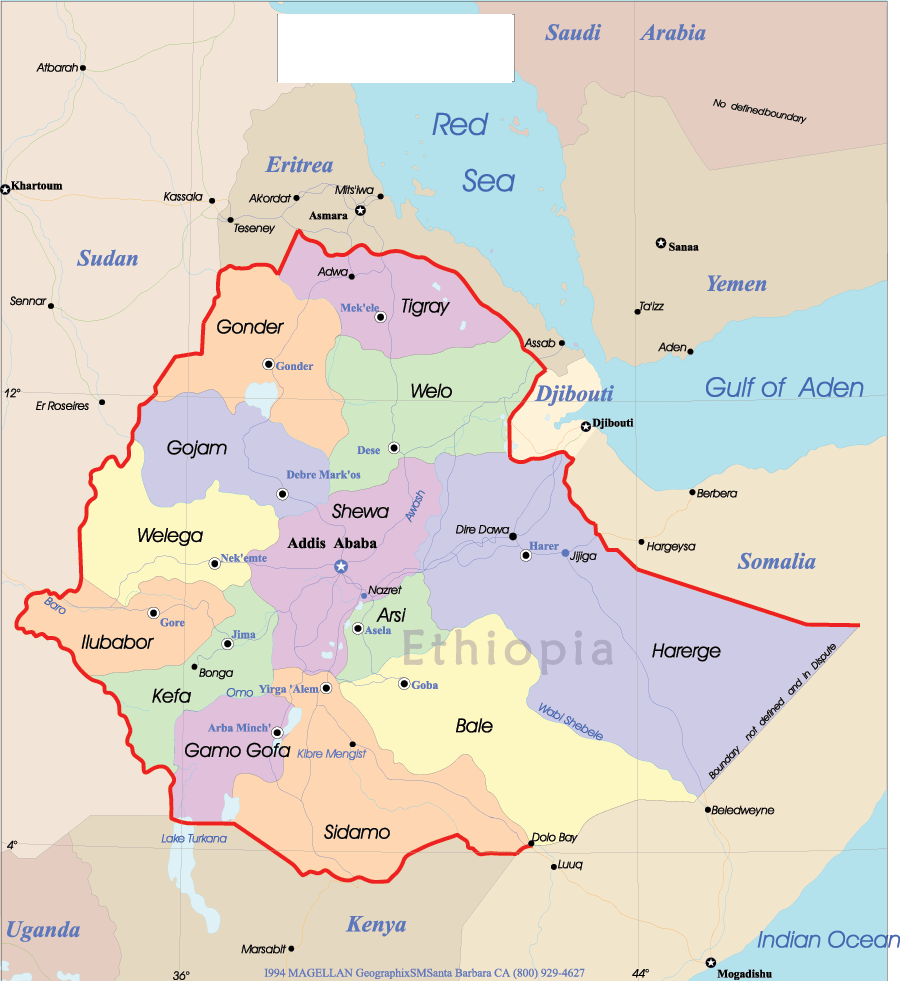
Ethiopia national map
Ethiopia physical and relief map
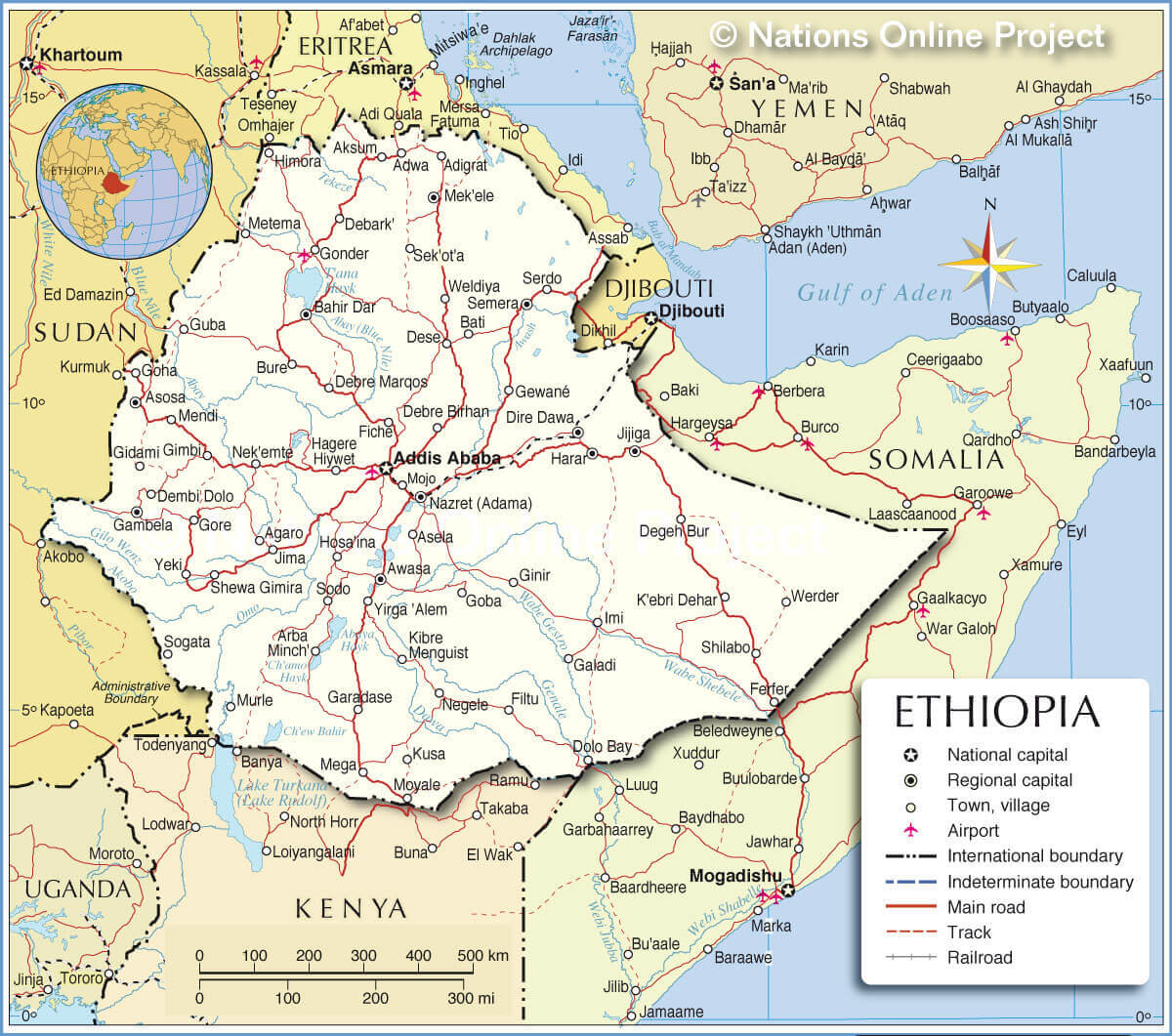
Ethiopia political map
Ethiopia population map
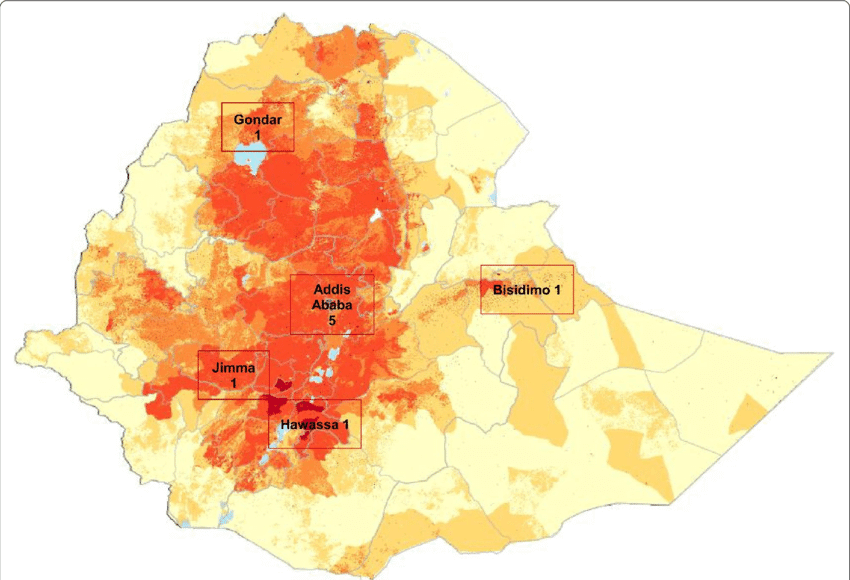
Ethiopia provinces map
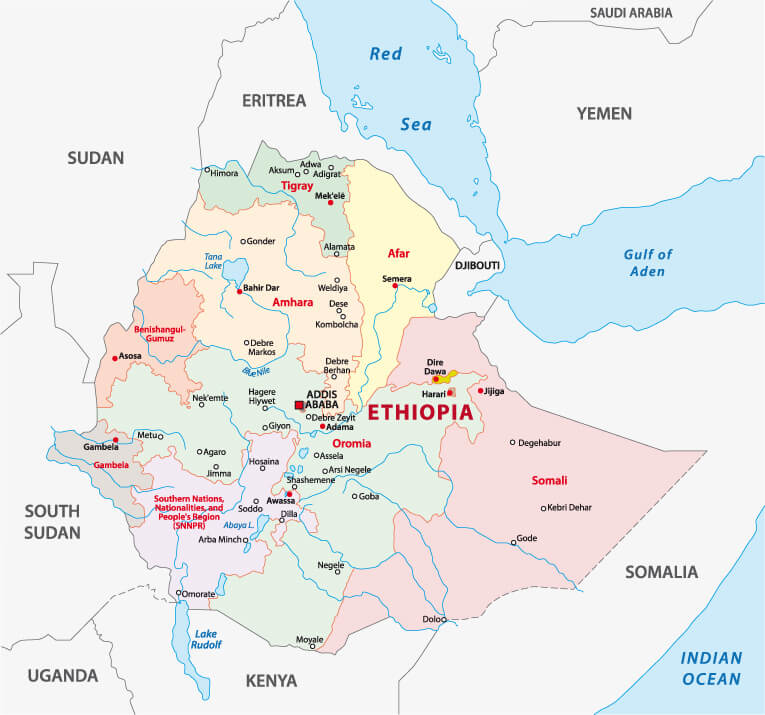
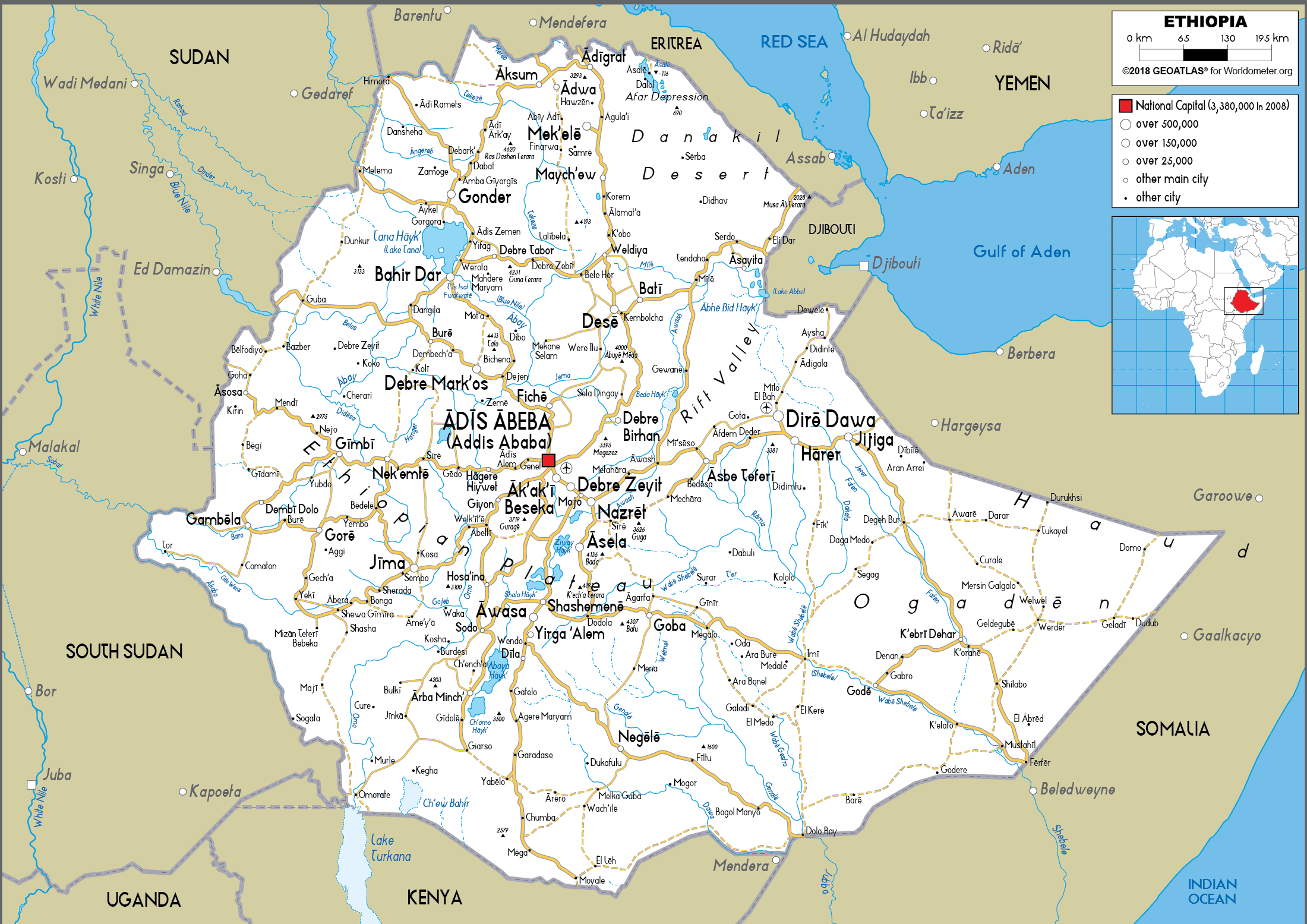
Ethiopia road map
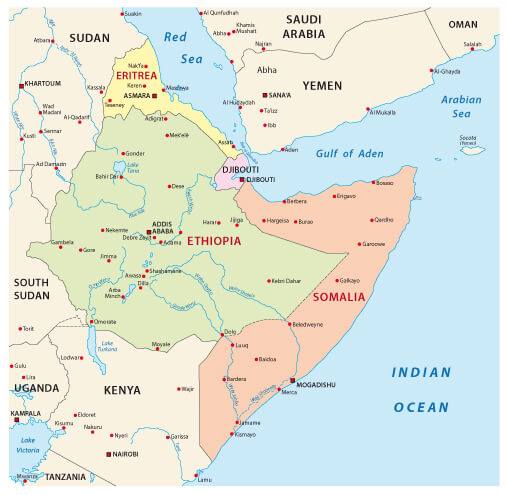
Ethiopia Somaili and Eritrea map
Ethiopia terrain map
Ethiopia

Ethiopian civil war map in 2020
Map of zones of Ethiopia
Political map of Ethiopia
The Kingdom of Aksum map

Feel free to explore these pages as well:
- Head of Performance Marketing
- Head of SEO
- Linkedin Profile: linkedin.com/in/arifcagrici
